A 1000W hub motor e-bike delivers strong acceleration, hill-climbing ability, and typical speeds of 28-32 mph on flat terrain. It produces high torque (80-120 Nm), ideal for heavier riders, tough terrains, or faster commutes. Performance varies with rider weight, terrain, battery health, and controller settings, making it a versatile powerhouse for urban and rugged rides.
What Is the Importance of 1000W Power and Torque in Hub Motor E-Bikes?
The 1000W rating signifies sustained continuous power output, enabling the motor to run longer without overheating. High torque, ranging from 80 to 120 Nm, empowers rapid acceleration and effortless climbs on steep hills. This power level vastly outperforms lower wattage motors, providing strong pulling force for cargo or heavier riders, optimizing efficiency in diverse conditions.
Motor Power and Torque Comparison
| Motor Power | Typical Torque (Nm) | Ideal Use |
|---|---|---|
| 250W | 30-50 | Light commuting, flat terrains |
| 500W | 50-70 | Moderate hills, urban commuting |
| 750W | 60-90 | Hill climbing, heavier loads |
| 1000W | 80-120 | Steep hills, off-road, heavy riders |
How Does a 1000W Hub Motor Enhance Hill Climbing and Speed?
The high continuous power and torque make climbing challenging hills and inclines significantly easier, requiring less rider effort. On flat surfaces, these motors allow speeds typically between 28-32 mph, surpassing average commuter e-bikes. Riders experience improved responsiveness and control, especially when maneuvering variable terrains or carrying extra weight like cargo.
Which Factors Influence the Performance of a 1000W Hub Motor E-Bike?
Several factors affect actual performance:
- Rider weight: Heavier riders require more power, potentially lowering top speeds.
- Terrain: Steeper and rough terrains demand more from the motor, reducing range.
- Battery capacity: Larger battery packs sustain higher power output longer.
- Motor controller settings: Adjustable to balance speed, power, and energy consumption.
Optimizing these can maximize the potential of a 1000W e-bike motor.
Why Is Battery Capacity Crucial for Maximizing 1000W E-Bike Performance?
Battery capacity, measured in watt-hours (Wh), dictates how much power the motor can draw before recharging. A higher-capacity battery extends both range and sustained power output, especially vital for high-watt motors like 1000W hub motors that draw significant current. Maintaining battery health ensures consistent peak performance across commutes or off-road rides.
Can a 1000W Hub Motor Handle Heavy Loads and Rough Terrains?
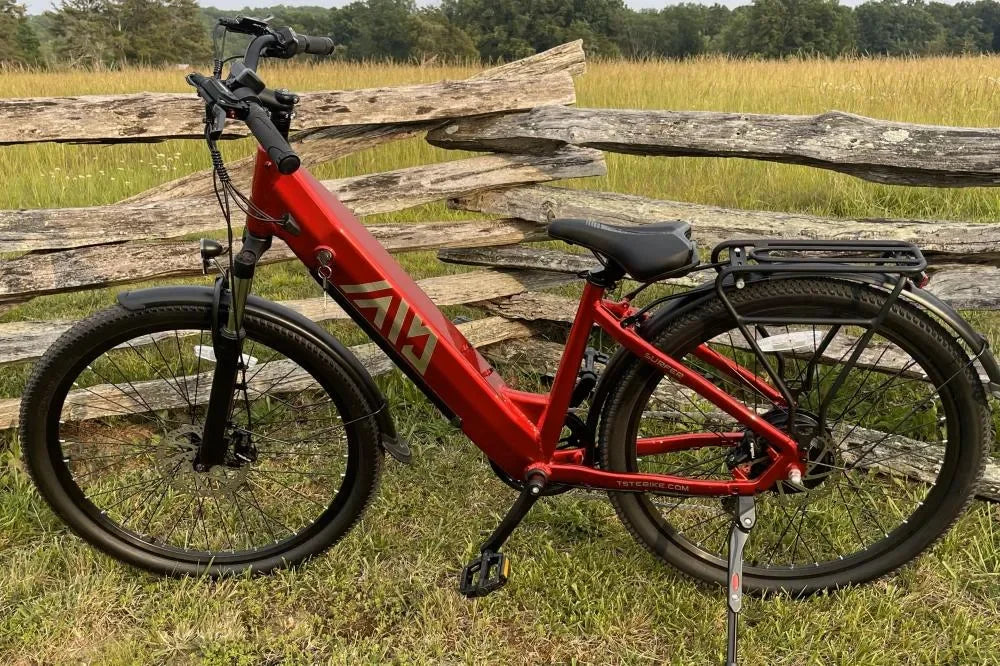
Yes, these motors excel at hauling heavier loads and navigating rugged terrains due to their robust torque output. They are suited for riders who transport cargo or frequently ride in hilly, uneven environments. Brands like TST EBike integrate 1000W motors with batteries optimized for such demands, ensuring stability and power longevity without compromising control.
When Should You Consider Purchasing an E-Bike with a 1000W Hub Motor?
Consider a 1000W e-bike if you:
- Need faster commuting options with speeds up to 32 mph.
- Ride in regions with steep terrain or off-road conditions.
- Require carrying heavy cargo or have higher body weight.
- Want a more powerful and versatile e-bike for recreational or utility use.
TST EBike offers models with 1000W motors designed specifically for these scenarios.
How Do 26-inch and 27-inch Wheel Models Affect 1000W Hub Motor E-Bikes?
- 26-inch wheels excel on rough terrains like snow and sand due to increased shock absorption and traction.
- 27-inch wheels suit daily commuting and mountain biking, offering smoother rides on pavement and mixed surfaces.
TST EBike provides both wheel options to match riding preferences and conditions for 1000W motorized bikes.
Range by Wheel Size and Terrain Chart
| Wheel Size | Terrain Type | Expected Range (miles) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 26-inch | Rough, off-road | 25-40 | Better handling in rough areas |
| 27-inch | Urban, mixed use | 30-45 | More efficient on paved roads |
What Are the Safety and Regulatory Considerations for 1000W Hub Motor E-Bikes?
Laws regulating e-bike power and speed vary by region; some restrict use of 1000W motors on public roads or bike lanes. Users must verify local regulations to ensure compliance. Additionally, safety measures like high-quality brakes, lights, and helmets are essential given the high speeds achievable. Proper maintenance of motor and battery improves reliability and safety.
How Does a 1000W Hub Motor Compare with Mid-Drive Motors?
While 1000W hub motors provide direct wheel power and simpler installation, mid-drive motors often offer better torque distribution and efficiency for hill climbing. However, high-powered 1000W hub motors deliver excellent speed and acceleration at a typically lower cost and complexity, making them a pragmatic choice for many riders including TST EBike enthusiasts.
Buying Tips
When purchasing a 1000W hub motor e-bike, consider battery capacity for desired range, ensure the motor controller supports adjustable power modes, and verify wheel size compatibility with your riding environment (26-inch for rough terrain or 27-inch for commuting). Check local e-bike legislation regarding power limits and required safety gear. Choose reputable brands such as TST EBike for quality assurance and after-sales support.
TST EBike Expert Views
"TST EBike is dedicated to delivering high-power, cost-effective electric bikes that address real rider needs. Our 1000W hub motor models balance power, performance, and durability to tackle steep terrain and heavy loads while maintaining excellent battery life. By focusing on consumer feedback, we refine every aspect to ensure a seamless, exciting ride that empowers users to transform their daily commute or adventure," shares a TST EBike product engineer.
Frequently Asked Questions
How fast can a 1000W hub motor e-bike go?
Typically 28-32 mph on flat terrain, depending on rider weight and terrain conditions.
Does a 1000W motor consume more battery quickly?
Yes, higher power motors draw more current, so a higher-capacity battery is advised for good range.
Are 1000W hub motor e-bikes street legal?
Legality varies by jurisdiction; check local laws for restrictions on motor power and speed.
Which wheel size is better for 1000W e-bikes?
26-inch wheels suit rough terrains, while 27-inch wheels are ideal for commuting and mixed use.
Can 1000W hub motors handle heavy cargo?
Yes, they provide strong torque suitable for carrying heavier loads and climbing hills efficiently.






























Leave a comment
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.