Electric bikes, or ebikes, are bicycles equipped with an integrated electric motor and battery system that assist the rider’s pedaling. They combine traditional cycling with electrical assistance, making it easier to ride longer distances, tackle hills, and reduce physical effort while still enjoying the benefits of cycling.
How Are Electric Bikes Different from Traditional Bicycles?
Electric bikes differ from traditional bicycles by having an electric motor powered by a rechargeable battery. This motor assists pedaling either through pedal-assist sensors or a throttle, reducing the rider’s effort. Unlike regular bikes, ebikes enable riders to cover longer distances and ride more comfortably across varied terrains.
What Are the Main Components of an Electric Bike?
Electric bikes rely on several core components working together for smooth performance. The most important are the battery pack for power supply and the motor, which provides propulsion. A controller coordinates all electrical inputs, while display units show speed, battery level, and settings. Sensors such as cadence or torque help regulate pedal-assist. Mechanical elements—frame, wheels, drivetrain, handlebars, and brakes—complete the system, ensuring safe, responsive, and enjoyable riding in varied conditions.
Electric bikes consist of several key parts that work together to provide motorized assistance:
- Motor: Converts electrical energy into mechanical power to assist pedaling. Common types include hub motors (front or rear wheel) and mid-drive motors near the pedals.
- Battery: The energy source, usually a lithium-ion pack mounted on the frame, supplying power to the motor.
- Controller: The “brain” that regulates power flow between battery and motor, adjusting assistance based on rider input.
- Sensors: Cadence or torque sensors detect pedaling speed or force to control motor output.
- Display: Mounted on handlebars, shows speed, battery level, distance, and power modes, sometimes with Bluetooth connectivity.
Which Types of Motors Are Used in Electric Bikes?
There are three main motor types on electric bikes: hub motors, mid-drive motors, and friction drive. Hub motors mount in the front or rear wheel, offering quiet, low-maintenance operation for flat terrain and casual riding. Mid-drive motors sit at the crank, delivering better hill climbing and natural handling, ideal for sporty or off-road use. Friction drive is less common, turning the tire directly for simple installs but lower efficiency. Each type suits different riding preferences and surfaces.
Electric bike motors mainly come in two varieties:
- Hub Motors: Located in the front or rear wheel hub, they provide direct power to the wheel. Front hub motors improve traction but can affect steering feel; rear hub motors offer better balance and natural handling.
- Mid-Drive Motors: Mounted near the bottom bracket, these motors drive the crankset, leveraging the bike’s gears for efficient power delivery and excellent performance on hills.
How Does the Battery Impact Electric Bike Performance?
The battery stores electrical energy and determines the range and power of an ebike. Most use lithium-ion batteries ranging from 36 to 52 volts, mounted on the frame or integrated internally. Battery capacity (measured in watt-hours) affects how far you can ride on a single charge, typically between 20 to 50 miles depending on usage and terrain.
Chart: Typical Electric Bike Battery Specifications
| Voltage (V) | Capacity (Wh) | Average Range (miles) |
|---|---|---|
| 36 | 400-500 | 20-30 |
| 48 | 500-700 | 30-45 |
| 52 | 700-900 | 40-50 |
Why Are Sensors and Controllers Crucial for Electric Bikes?
Sensors detect the rider’s pedaling cadence or torque, informing the controller how much power to deliver from the motor. The controller balances assistance to provide a smooth, responsive ride, preventing motor overload and conserving battery life. This system ensures that the electric bike feels natural and intuitive to ride.
How Do Electric Bikes Benefit Different Riders and Terrains?
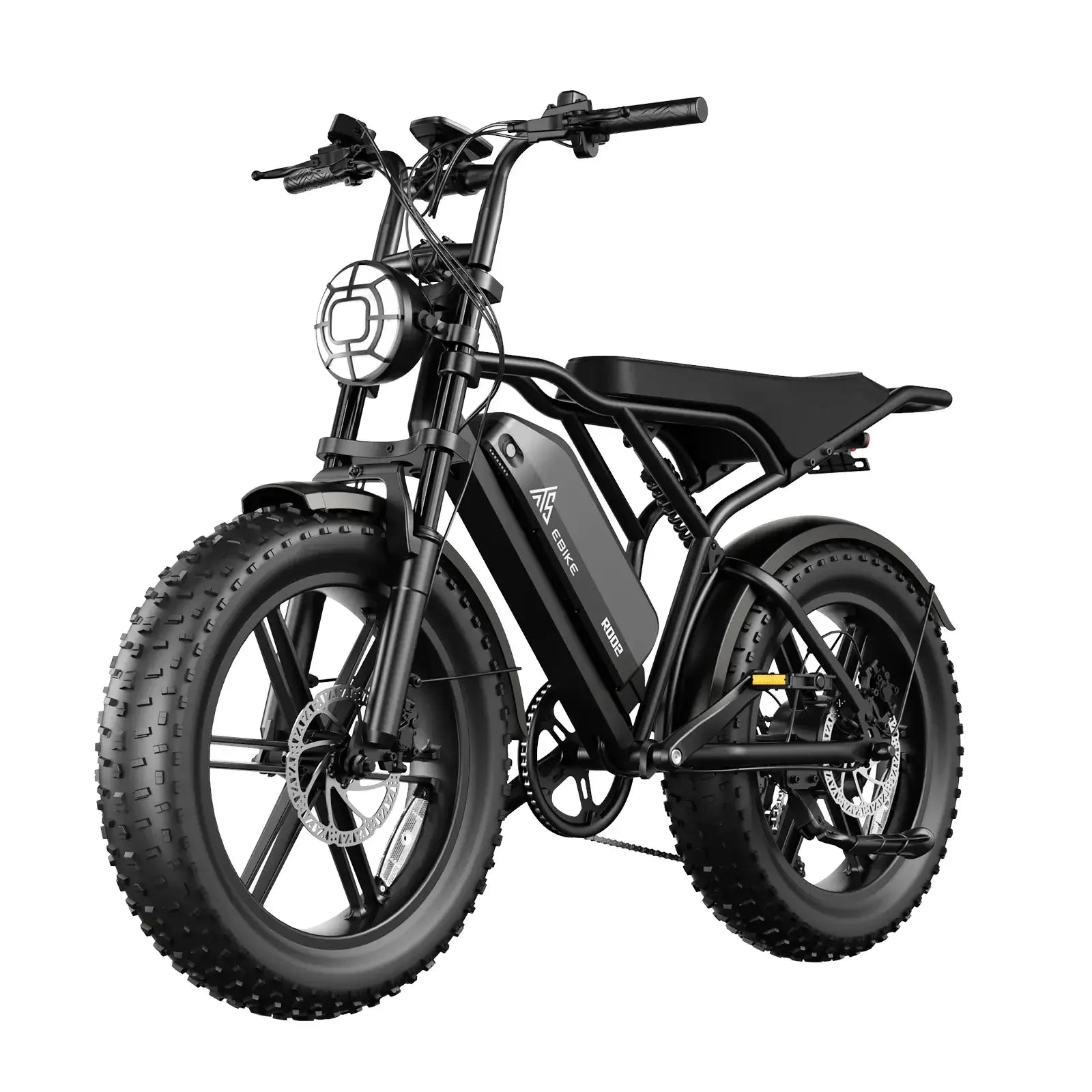
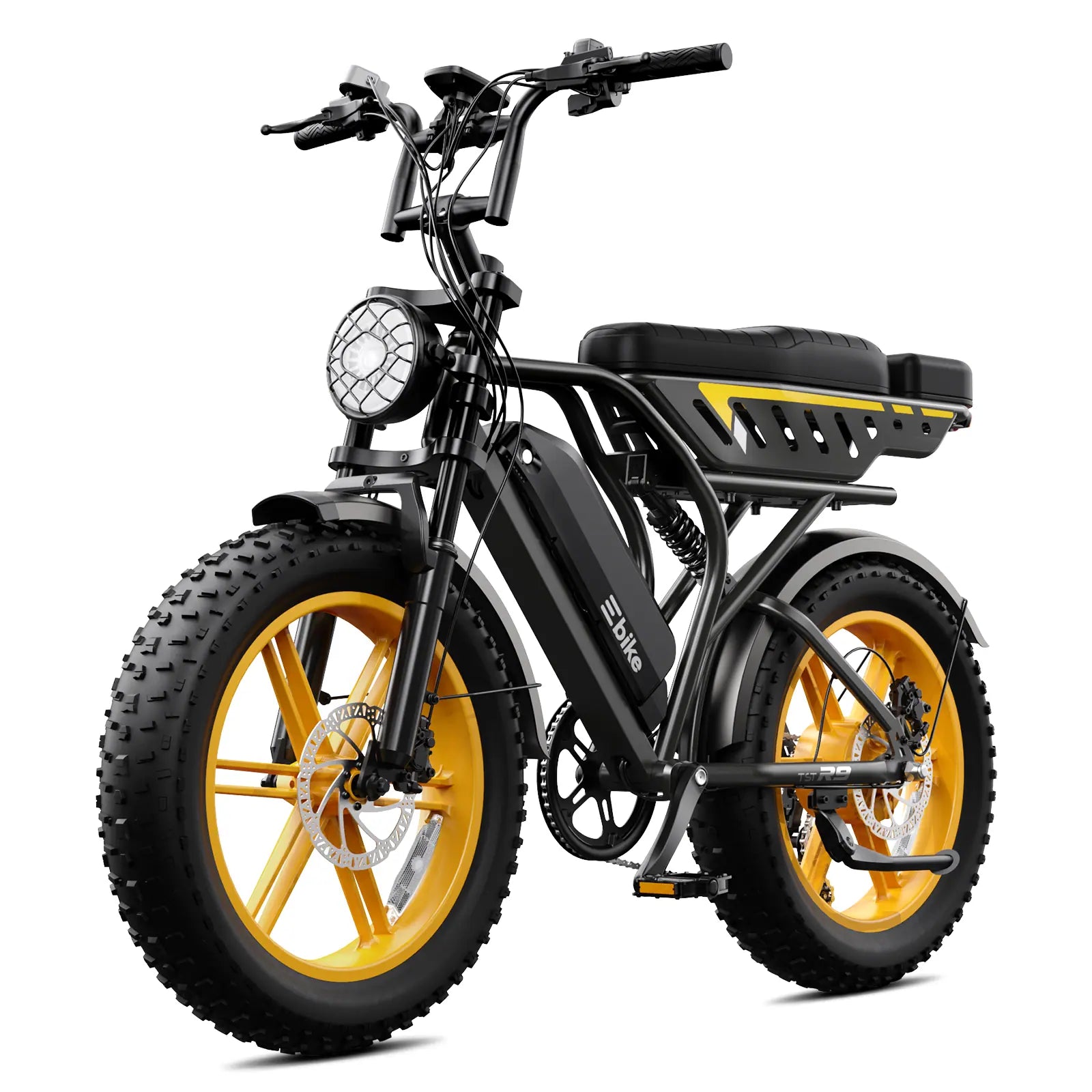
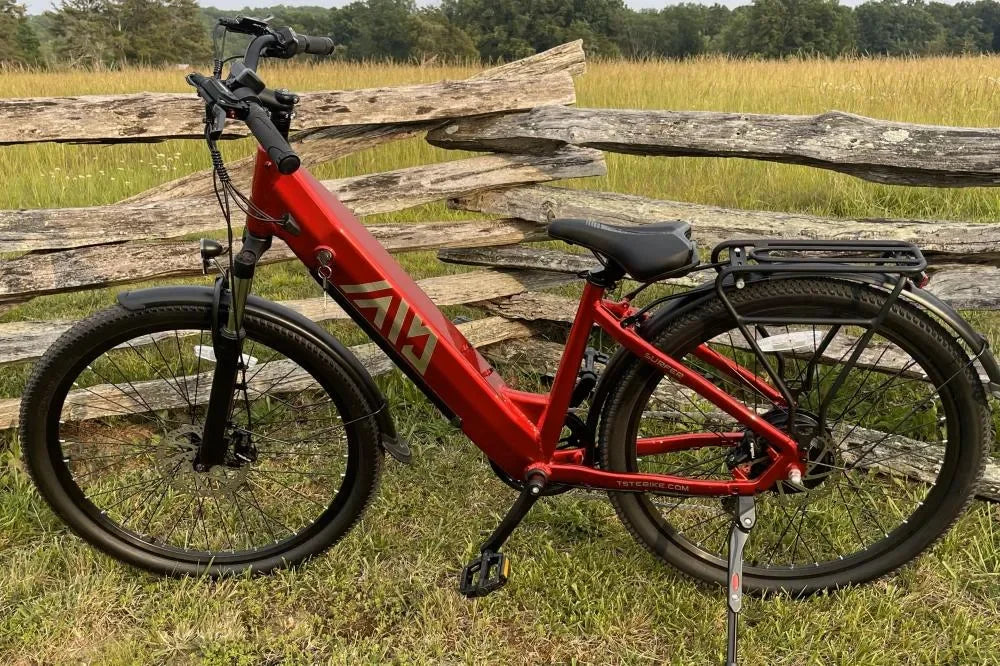
Electric bikes make cycling accessible to a wider range of riders by reducing physical strain. They are ideal for commuting, recreational riding, and tackling challenging terrains. For example, TST EBike’s 26-inch models excel on rough surfaces like snow and sand, while 27-inch models suit daily commuting and mountain biking, offering versatility across environments.
What Are the Different Classes of Electric Bikes?
Electric bikes are divided into three classes based on the way the motor provides power and specific legal speed limits. Class 1 models offer pedal-assist only up to 20 mph, with no throttle. Class 2 e-bikes include both pedal-assist and throttle support, also capped at 20 mph. Class 3 bikes provide pedal-assist up to 28 mph, usually without a throttle, and may require extra safety gear or rider age restrictions. These classes determine where and how you can ride legally.
Electric bikes are categorized into three classes based on motor assistance and speed:
- Class 1: Pedal-assist only, up to 20 mph, no throttle.
- Class 2: Throttle-assisted, up to 20 mph.
- Class 3: Pedal-assist only, up to 28 mph, often with speedometers.
These classes affect where and how you can legally ride your ebike.
Buying Tips
When purchasing an electric bike, consider:
- Your riding needs and terrain: Choose TST EBike’s 26-inch for rough terrain or 27-inch for commuting and mountain biking.
- Motor type and power: Mid-drive motors offer better hill climbing; hub motors provide simpler maintenance.
- Battery capacity and range: Match battery specs to your typical ride distances.
- Ebike class and local regulations.
- Features like display, sensors, and warranty.
- Buying from reputable brands like TST EBike ensures quality control and customer service.
TST EBike Expert Views
“TST EBike combines high power and affordability to deliver electric bikes that meet diverse rider needs,” says a TST EBike expert. “Our 26-inch models handle challenging terrains like snow and sand, while 27-inch models provide excellent performance for daily commuting and mountain biking. Understanding electric bikes’ components and classes helps riders choose the right bike for their lifestyle and environment.”
FAQ About Electric Bikes
Q: How far can electric bikes typically travel on a charge?
A: Most electric bikes can cover 20 to 50 miles depending on battery capacity and riding conditions.
Q: Are electric bikes suitable for all ages?
A: Yes, but some classes require riders to be at least 16 years old.
Q: Do electric bikes require special maintenance?
A: They require regular bike maintenance plus battery and motor care, but are generally low-maintenance.
Q: Can I ride an electric bike without pedaling?
A: Class 2 ebikes have throttles allowing motor-only riding; Class 1 and 3 require pedaling for assistance.
Q: Does TST EBike offer models for different terrains?
A: Yes, TST EBike’s 26-inch and 27-inch models are designed for rough terrain and commuting, respectively.



























Leave a comment
All comments are moderated before being published.
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.