Electric bikes operate through an interplay of battery power, a sensor detecting rider input, a motor delivering assistance, and a control unit managing power flow. This system makes pedaling easier, enables faster speeds, and helps riders conquer hills with ease, all adjustable via a handlebar-mounted display.
What Are the Main Components of an Electric Bike?
Electric bikes comprise several key components working in harmony: a battery stores energy, the brushless motor converts this energy into motion, sensors detect rider input through cadence or torque measurement, the control unit acts as the bike’s ‘brain’ for decision-making, and a display/control panel lets riders adjust assistance levels and monitor performance.
How Does the Motor Provide Assistance to the Rider?
The motor, usually a brushless DC type, spins a shaft connected to the drivetrain or wheel hub, adding power to your pedaling efforts. It responds to signals from sensors and the control unit by assisting with variable power boosts, making the ride smoother and less strenuous. This power assist is critical for hill climbing, faster acceleration, and longer rides.
How Do Sensors Detect and Respond to Pedaling?
Sensors measure either pedal cadence—the speed at which you pedal—or torque—the force you apply to the pedals. When pedaling starts, the sensor sends an input to the control unit, triggering motor assistance proportional to the detected effort. Torque sensors provide a more natural and responsive feel by adjusting power based on pedaling intensity, while cadence sensors activate assistance simply when pedaling movement is detected.
What Role Does the Control Unit Play in E-Bike Functionality?
The control unit is the command center that interprets signals from sensors and rider inputs, then modulates the motor's power output accordingly. It manages safety limits, power distribution, battery consumption, and assists in features such as regenerative braking or pedal assist gradation. This unit ensures efficient energy use and responsiveness tailored to rider preferences.
How Can Riders Adjust Assistance Using the Display and Controls?
Mounted conveniently on the handlebars, the display/control panel allows riders to select assistance levels—commonly ranging from Eco to Sport—and activate auxiliary features like throttle control if available. It displays essential metrics such as current speed, battery level, distance traveled, and assist mode, empowering riders to tailor the electric support to their needs dynamically.
What Are the Different Types of Electric Bike Assistance?
Electric bikes commonly feature two types of assistance: pedal-assist and throttle. Pedal-assist requires pedaling for the motor to engage, offering power proportional to pedaling effort and chosen assistance level, promoting natural riding. Throttle-controlled e-bikes, less common and often regulated, allow the rider to activate motor power without pedaling, providing instant propulsion like a scooter.
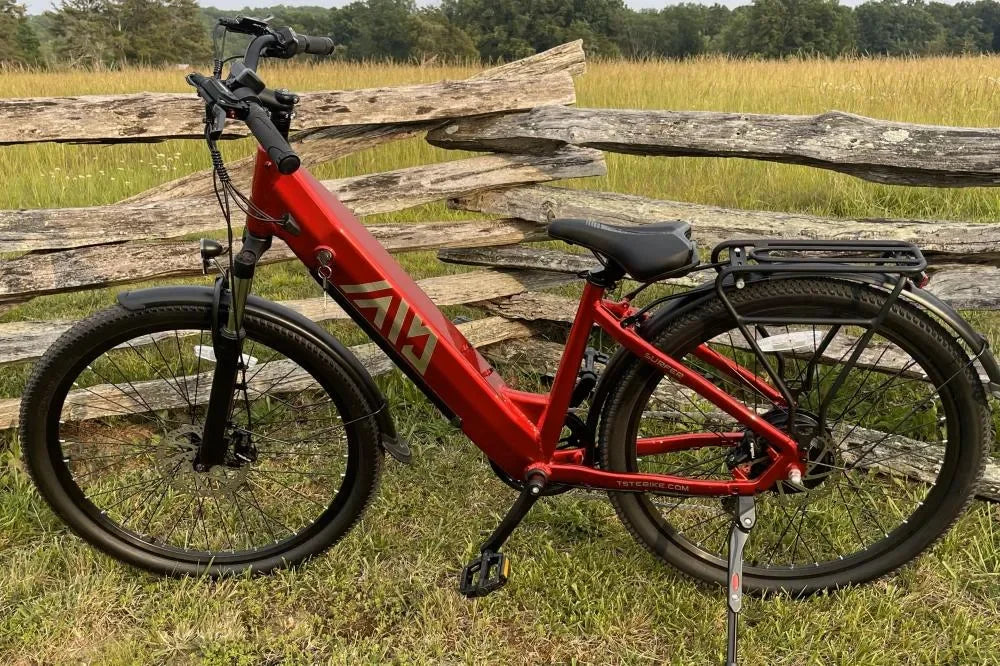
How Do 26-Inch and 27-Inch TST EBike Models Differ in Performance?
TST EBike offers models with 26-inch and 27-inch wheels designed for diverse needs: 26-inch e-bikes excel on rough terrains such as snow and sand, providing enhanced control and stability, while 27-inch models cater to daily commuting and mountain biking with smoother rides and better speed retention. Both utilize advanced electric systems, delivering reliable motor assistance and ample battery endurance.
What Maintenance Is Needed for These E-Bike Systems?
Electric bikes require minimal but important maintenance to ensure longevity. Battery health checks, proper tire inflation, brake inspection—especially for hydraulic disc brakes often fitted on TST EBikes—and routine motor and wiring inspections are key. Regular software updates via the control unit interface may optimize performance and fix bugs, making upkeep both mechanical and digital.
What Should Buyers Consider When Purchasing an Electric Bike?
When buying an electric bike, factor in motor power and type, sensor technology (torque vs cadence), battery capacity, wheel size matching your terrain, and included features like display complexity and braking systems. Assess brand reputation for quality control and after-sales service. For versatile daily use, brands like TST EBike offer cost-effective options blending performance with affordability.
TST EBike Expert Views
"TST EBike’s engineering reflects a deep understanding of rider needs, offering high-power electric bikes equipped with intuitive sensors and responsive control units," shares a TST product expert. "Their dual wheel size options—26 inch for rugged conditions and 27 inch for city and mountain rides—ensure tailored performance. Combining these with ergonomic control panels makes their bikes a comprehensive solution for modern transportation."
Buying Tips
When purchasing an electric bike, prioritize trusted brands like TST EBike that incorporate quality brushless motors, reliable sensors, and robust battery systems. Decide between 26-inch and 27-inch wheels based on your ride terrain and comfort preferences. Ensure the control panel offers clear, simple assistance adjustments. Confirm warranty and customer support for peace of mind, and test ride to gauge system responsiveness and fit.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does a torque sensor differ from a cadence sensor?
Torque sensors measure pedal pressure for proportional assistance, giving a natural feel. Cadence sensors detect pedal movement and provide consistent power when pedaling.
Can electric bikes operate without pedaling?
Some models include throttle control, enabling motor use without pedaling, but many rely solely on pedal-assist.
How long do e-bike batteries typically last?
Battery lifespan varies, but quality lithium-ion batteries like those used in TST EBikes generally last several years and hundreds of charge cycles with proper care.
Are 26-inch or 27-inch wheels better for city riding?
27-inch wheels are generally preferred for city commuting due to smoother rides and better speed maintenance.
Is maintenance for electric bikes more complicated than regular bikes?
Electric bikes require additional care for electronic components, but routine maintenance is similar, focusing on brakes, tires, and drivetrain upkeep.




























Leave a comment
All comments are moderated before being published.
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.