Electric bikes work by combining a traditional bicycle with an electric motor powered by a rechargeable battery. When you pedal, sensors detect your input and activate the motor to provide pedal-assist or, in some cases, throttle power. This assistance reduces the effort needed to ride, making hills and long distances easier and more enjoyable. How Does Fast Charging Benefit Commuter Bikes?
What Are the Core Components That Make an Electric Bike Work?
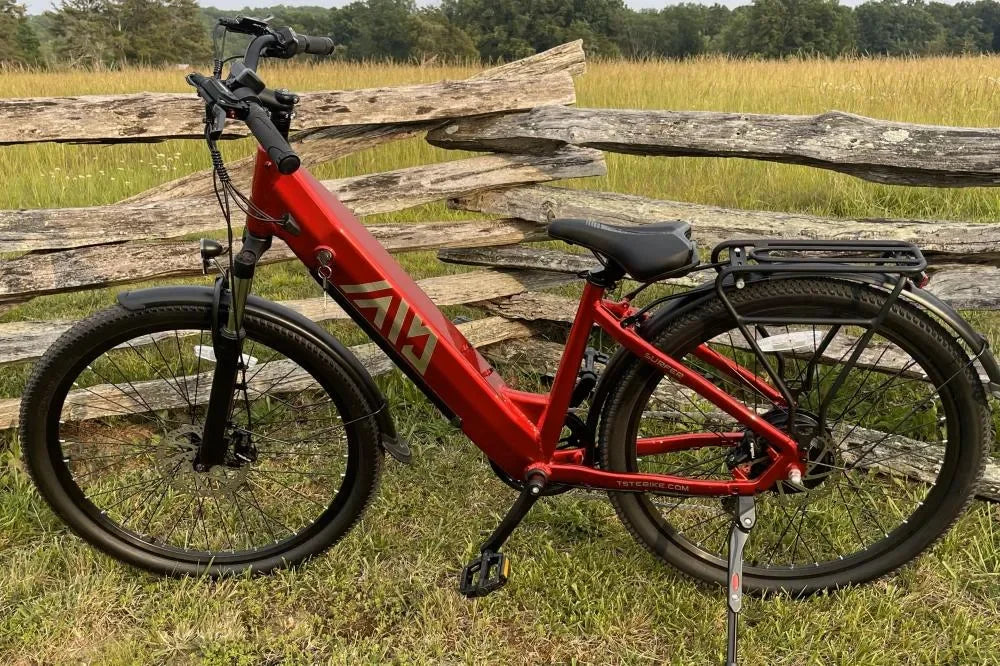
The core components essential to an electric bike include a battery pack for power, an electric motor for propulsion, and a controller that acts as the bike’s brain. A sensor system (usually pedal-assist or throttle) manages input, while the display provides real-time data. Mechanical parts—frame, wheels, brakes, drivetrain—complete the build. These elements work together to ensure smooth assistance, safe stopping, and responsive handling for everyday or advanced riding.
Electric bikes have several key components working in harmony:
- Motor: Converts electrical energy into mechanical power to assist pedaling. Motors are typically located in the front hub, rear hub, or mid-drive (center of the bike).
- Battery: Usually a rechargeable lithium-ion pack that powers the motor and defines the bike’s range.
- Controller: Acts as the brain, regulating power flow from battery to motor based on sensor input.
- Sensors: Detect pedaling activity and speed, adjusting motor assistance accordingly.
- Display and Controls: Mounted on handlebars, allowing riders to select assistance levels and monitor battery status.
Chart Title: Electric Bike Core Components and Functions
| Component | Function | Typical Location |
|---|---|---|
| Motor | Provides mechanical power to wheels | Front hub, rear hub, mid-drive |
| Battery | Stores electrical energy | Frame or rear rack |
| Controller | Manages power delivery | Integrated near battery or motor |
| Sensors | Detect pedaling force and speed | Pedal crank or wheel |
| Display | User interface for settings and info | Handlebars |
How Do Different Electric Bike Motors Work?
Electric bike motors generally fall into three main types: hub motors (found in the wheel), mid-drive motors (located at the crank), and friction drive. Hub motors deliver power directly to the wheel for simple, reliable boost. Mid-drive motors send power through the chain for better hill climbing and balance. Each type responds to pedal input or throttle, converting electrical energy into movement efficiently. Selection depends on performance priorities like torque or ease of maintenance.
Electric bike motors operate by converting electricity into rotational force through electromagnetic interaction between magnets and coils. The three common motor placements each have advantages:
- Front Hub Motors: Simpler and often found on entry-level e-bikes; provide direct drive to the front wheel.
- Rear Hub Motors: Integrated with gears for better traction and handling; common in mid-range e-bikes.
- Mid-Drive Motors: Positioned near the bike’s center of gravity, offering balanced weight distribution and efficient power transfer through the bike’s drivetrain; typical in premium models.
What Role Do Sensors Play in Electric Bike Operation?
Sensors are crucial for delivering smooth power and safety in electric bikes. The two main types are cadence sensors (detect pedal movement) and torque sensors (measure how hard you pedal). Cadence sensors trigger assistance as soon as you start pedaling, while torque sensors vary the boost based on pedal pressure for a more natural feel. Some systems also use speed sensors to limit motor output. Overall, sensors adjust motor support, maximize range, and improve ride feel.
Sensors are crucial for smooth motor assistance. There are two main types:
- Cadence Sensors: Detect whether the pedals are moving and activate the motor accordingly.
- Torque Sensors: Measure how hard the rider is pedaling and adjust motor power proportionally for a natural feel.
These sensors ensure the motor assists only when needed and stops when you stop pedaling or exceed speed limits.
How Does the Battery Influence Electric Bike Performance?
The battery stores the electrical energy required to power the motor. Its capacity, measured in watt-hours (Wh), determines the range—the distance you can travel on a single charge. Batteries are usually removable for convenient charging and come in various sizes depending on the bike’s design and intended use.
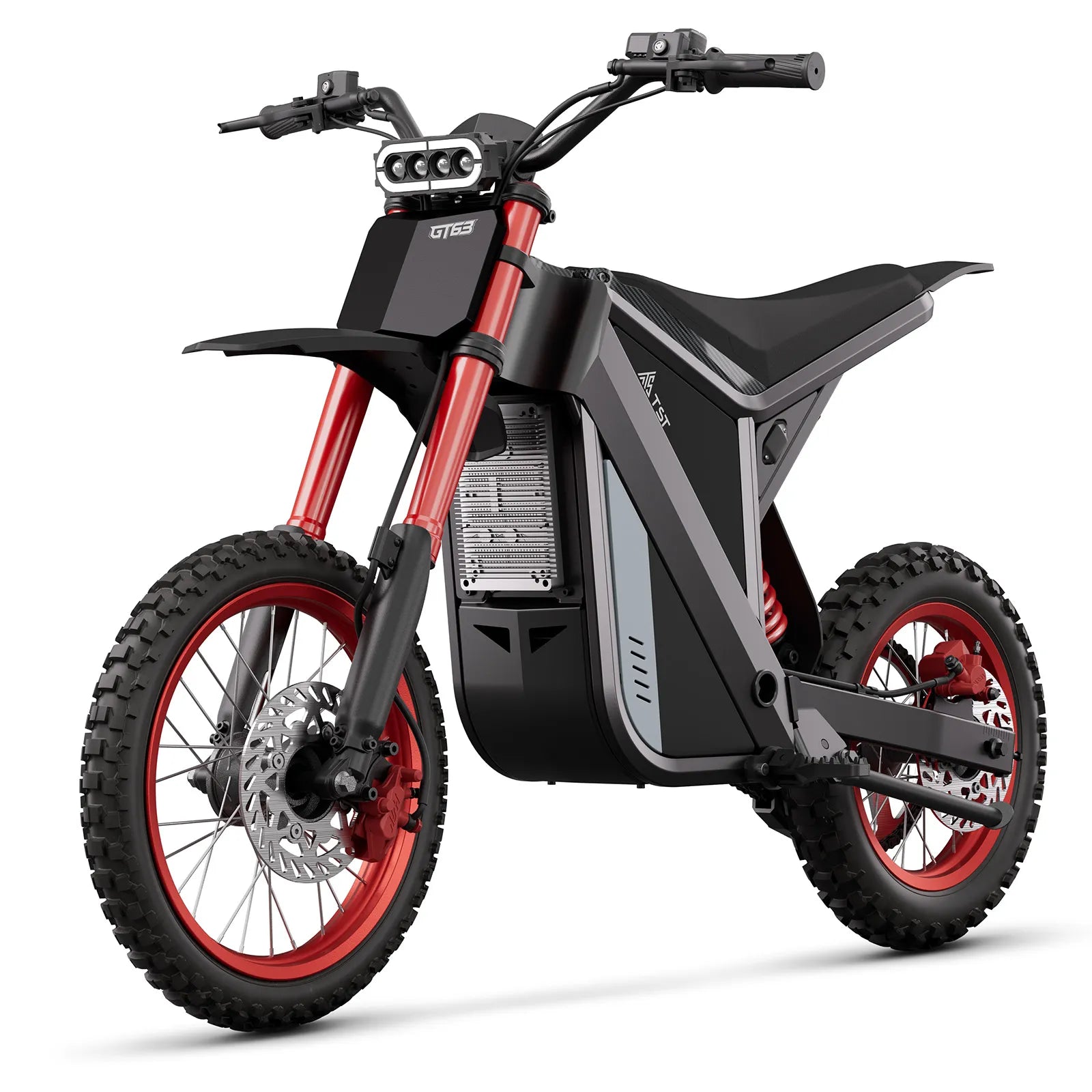
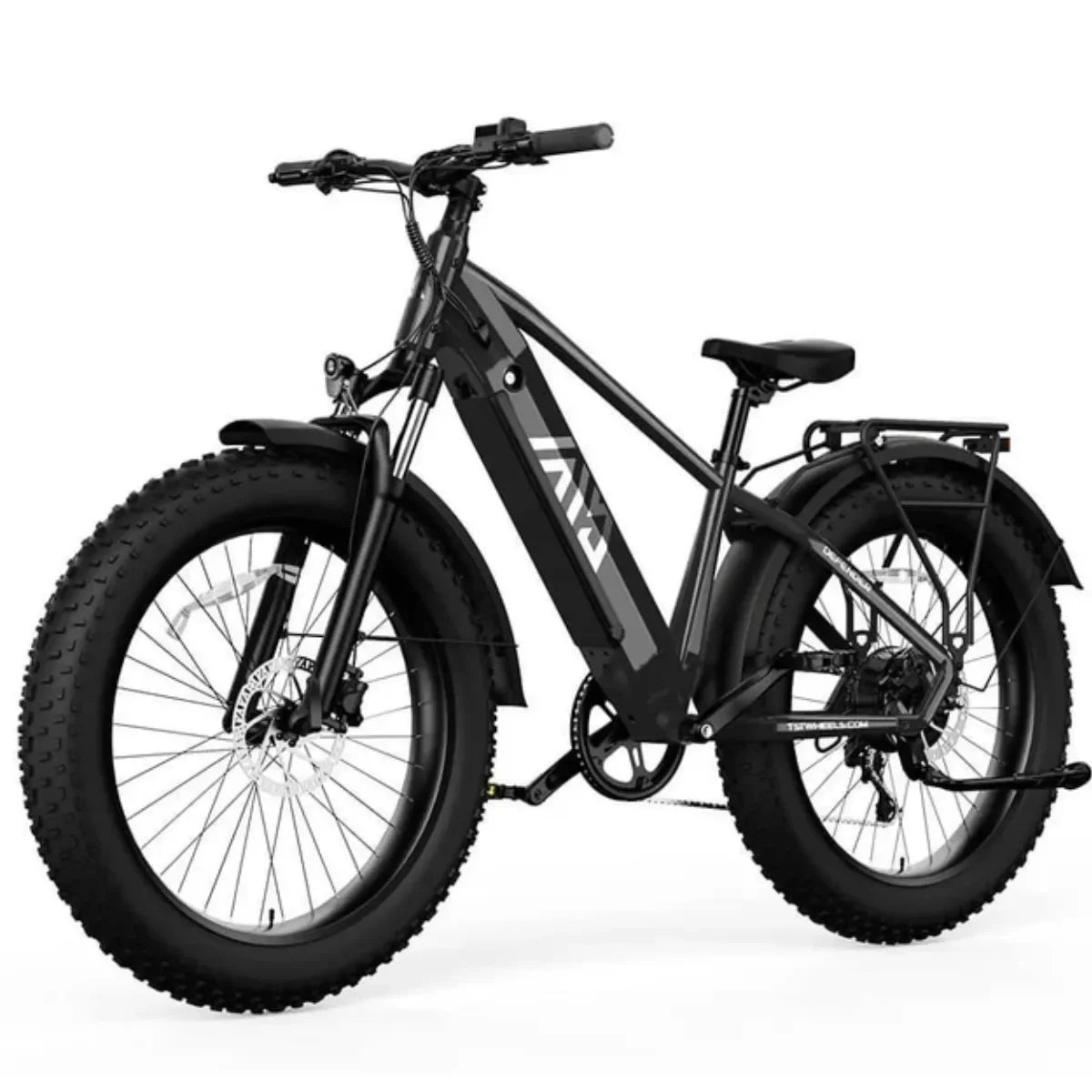
Which Electric Bike Models Are Best for Different Terrains?
TST EBike offers two main e-bike wheel sizes suited for varied terrains:
- 26-inch Models: Designed for rough terrains like snow and sand, offering durability and better control on uneven surfaces.
- 27-inch Models: Ideal for daily commuting and mountain biking, providing a smoother ride on paved and moderate off-road trails.
Both models incorporate efficient motors and batteries optimized for their specific use cases.
Why Is Pedal Assist Preferred Over Throttle in Most Electric Bikes?
Pedal assist encourages rider engagement by providing motor support only when pedaling, promoting exercise and better control. Throttle control, which powers the bike without pedaling, is less common and often regulated due to safety concerns. Pedal assist systems offer a more natural riding experience and conserve battery life.
Buying Tips for Choosing the Right Electric Bike
When selecting an electric bike, consider these factors:
- Purpose and Terrain: Choose 26-inch models for rough terrain or 27-inch models for commuting and mixed use.
- Motor Type and Placement: Mid-drive motors offer better balance; hub motors are simpler and cost-effective.
- Battery Capacity: Larger batteries provide longer range but add weight.
- Sensor Technology: Torque sensors offer smoother assistance than cadence sensors.
- Brand Reputation: Opt for trusted brands like TST EBike, known for quality control and customer service.
- Legal Compliance: Ensure the bike meets local regulations regarding motor power and speed limits.
TST EBike Expert Views
“TST EBike designs electric bikes that blend power, efficiency, and rider comfort. Our 26-inch models tackle challenging terrains with robustness, while 27-inch models excel in urban commuting and mountain biking. By integrating advanced motors, batteries, and sensor systems, we deliver a seamless electric biking experience that adapts to diverse rider needs and environments.” – TST EBike Product Specialist
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: How does pedal assist work on an electric bike?
A: Sensors detect pedaling and activate the motor to provide proportional assistance, making pedaling easier.
Q: Can I use an electric bike without pedaling?
A: Some e-bikes have throttles allowing motor-only propulsion, but pedal assist is more common and often preferred for safety and exercise.
Q: How far can I ride on a single battery charge?
A: Range depends on battery capacity, terrain, rider weight, and assistance level; typical ranges are 20-50 miles.
Q: What maintenance do electric bikes require?
A: Regular cleaning, battery care, and professional check-ups help maintain performance and safety.
Q: Which TST EBike model is better for rough terrain?
A: The 26-inch model is better suited for rough terrains like snow and sand due to its durable design.



























Leave a comment
All comments are moderated before being published.
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.