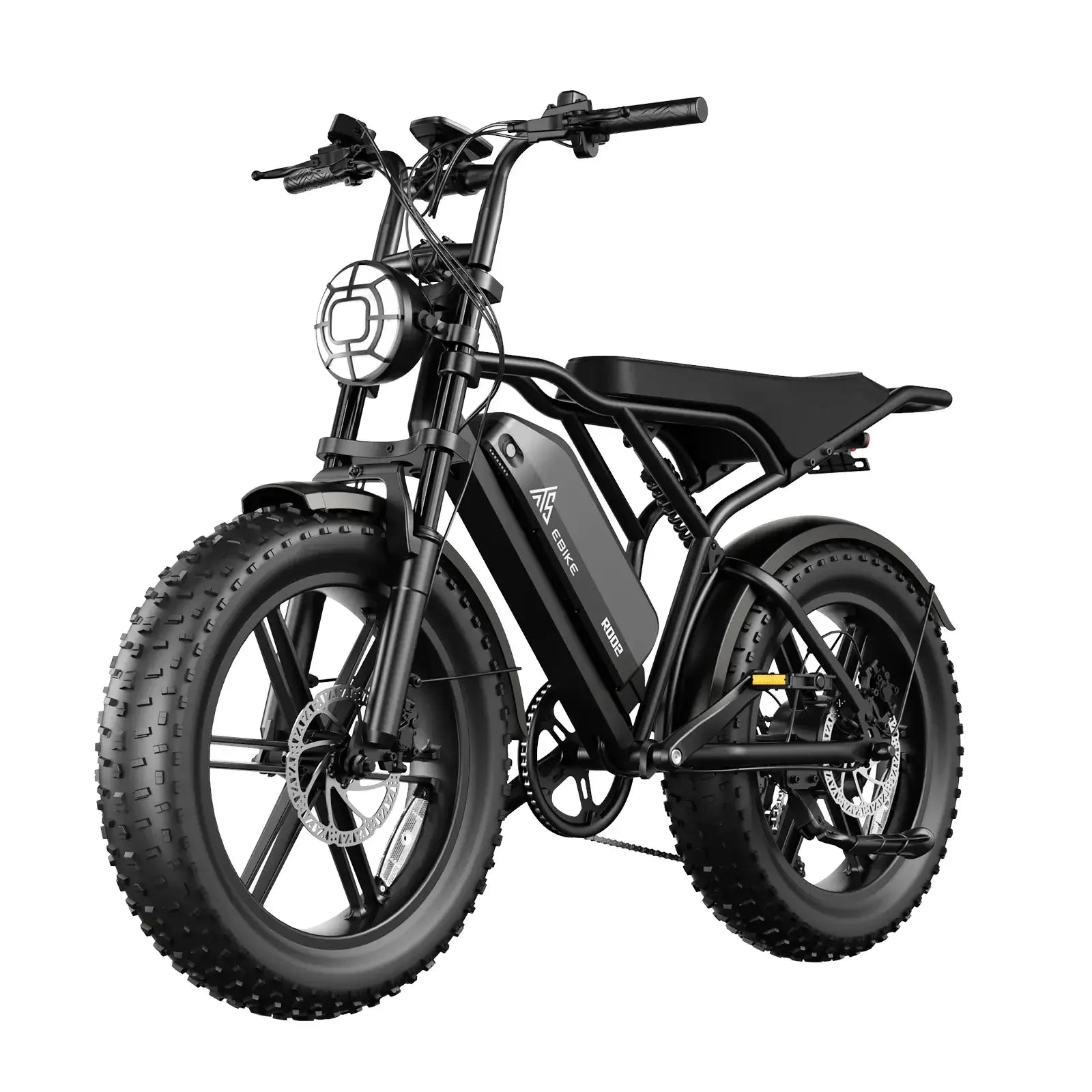
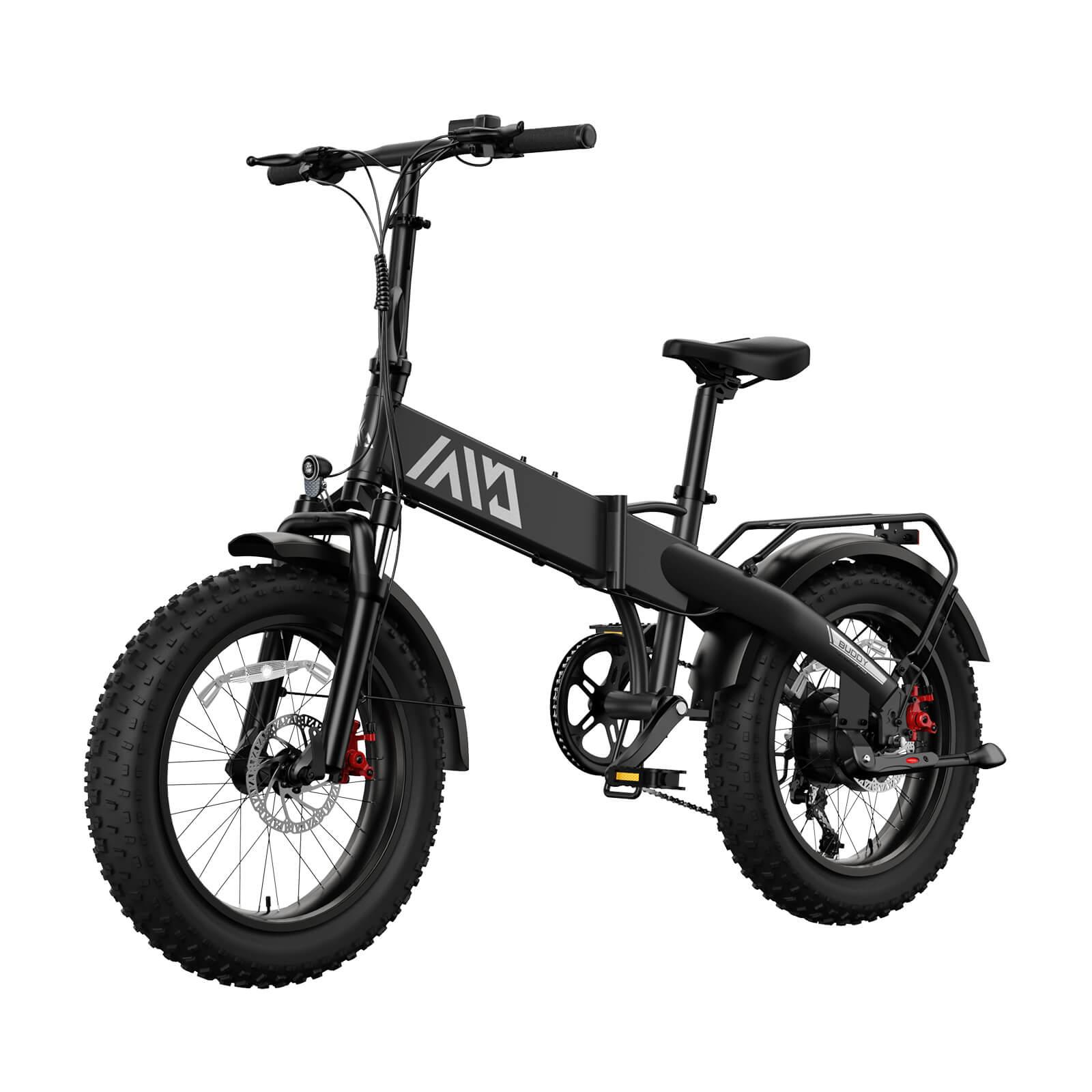
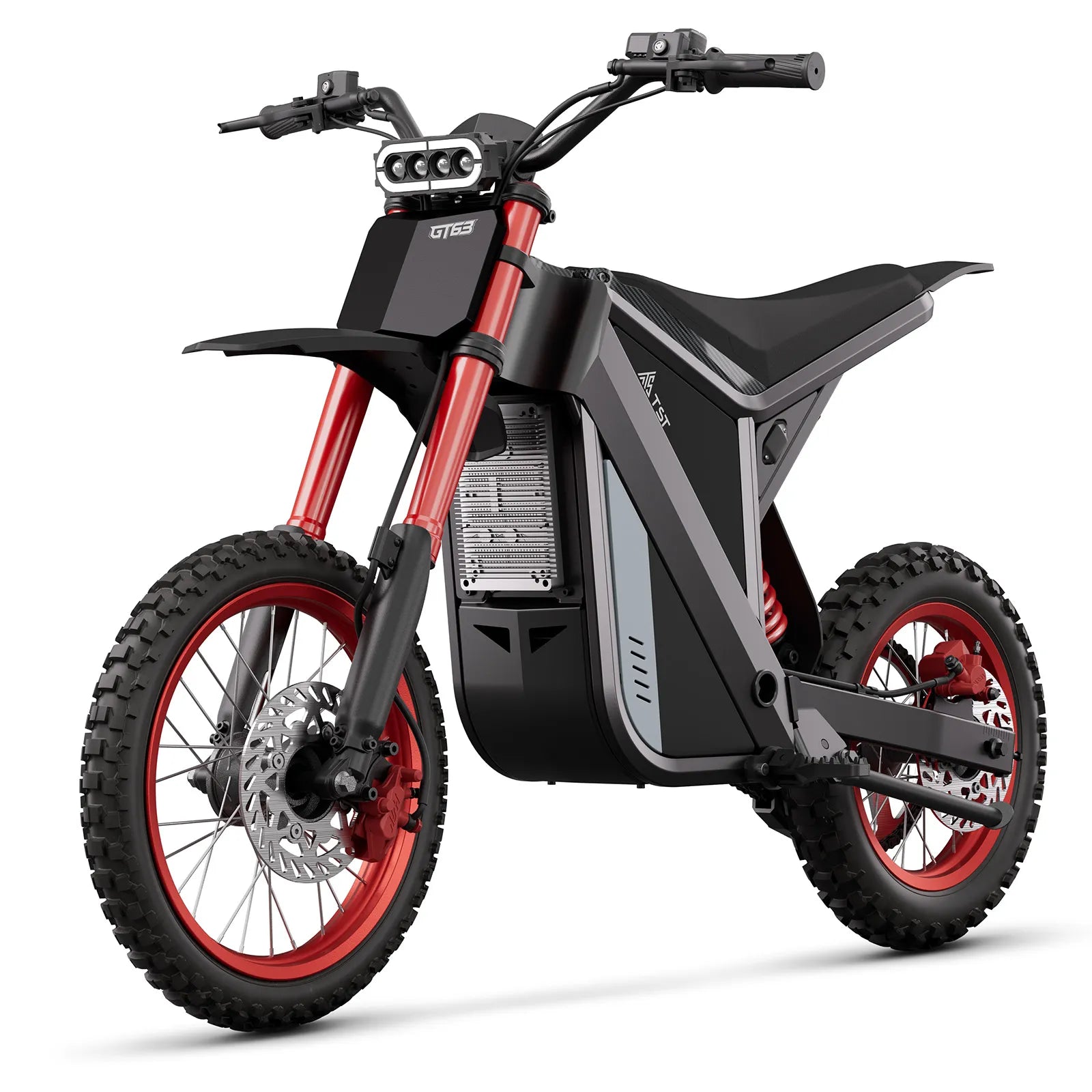
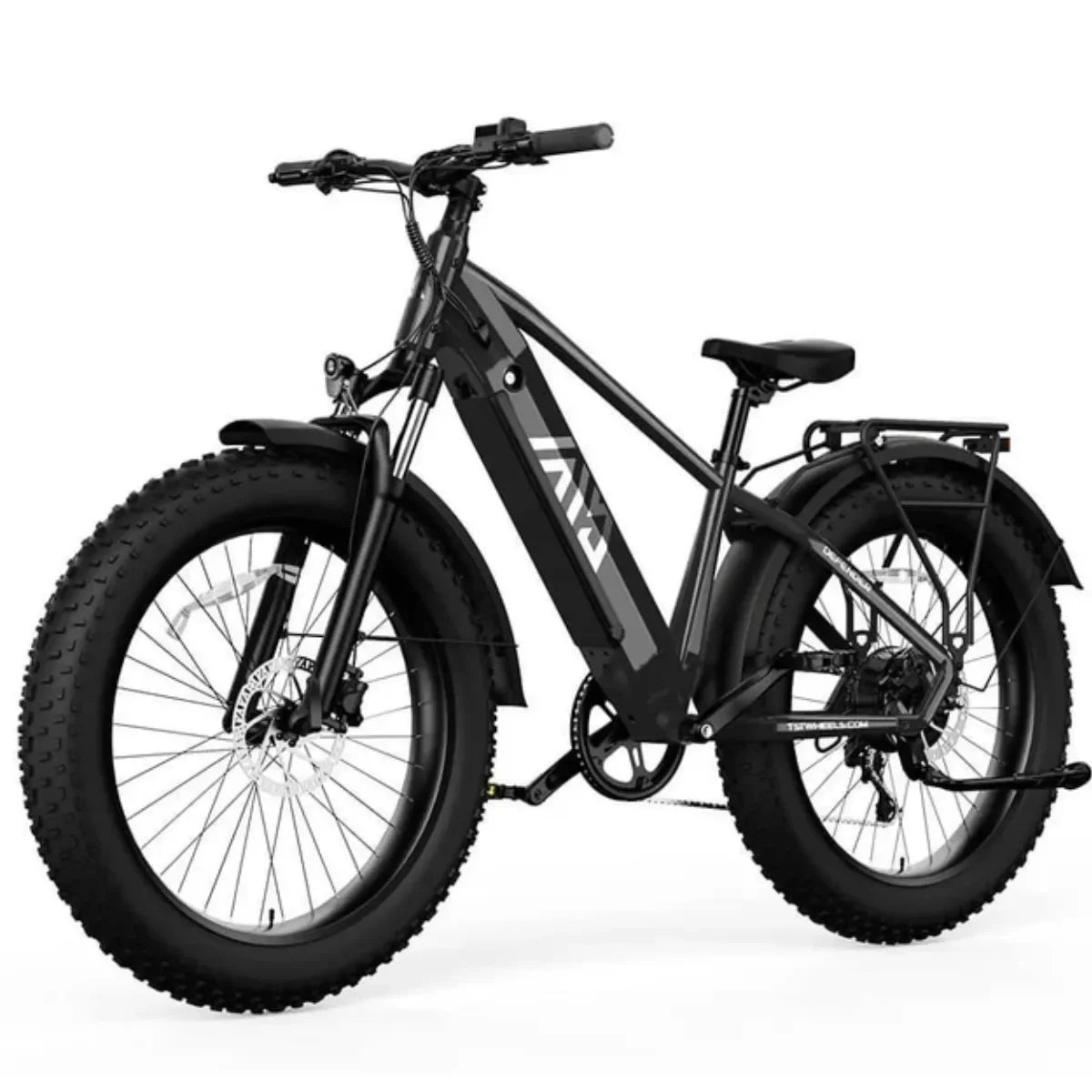
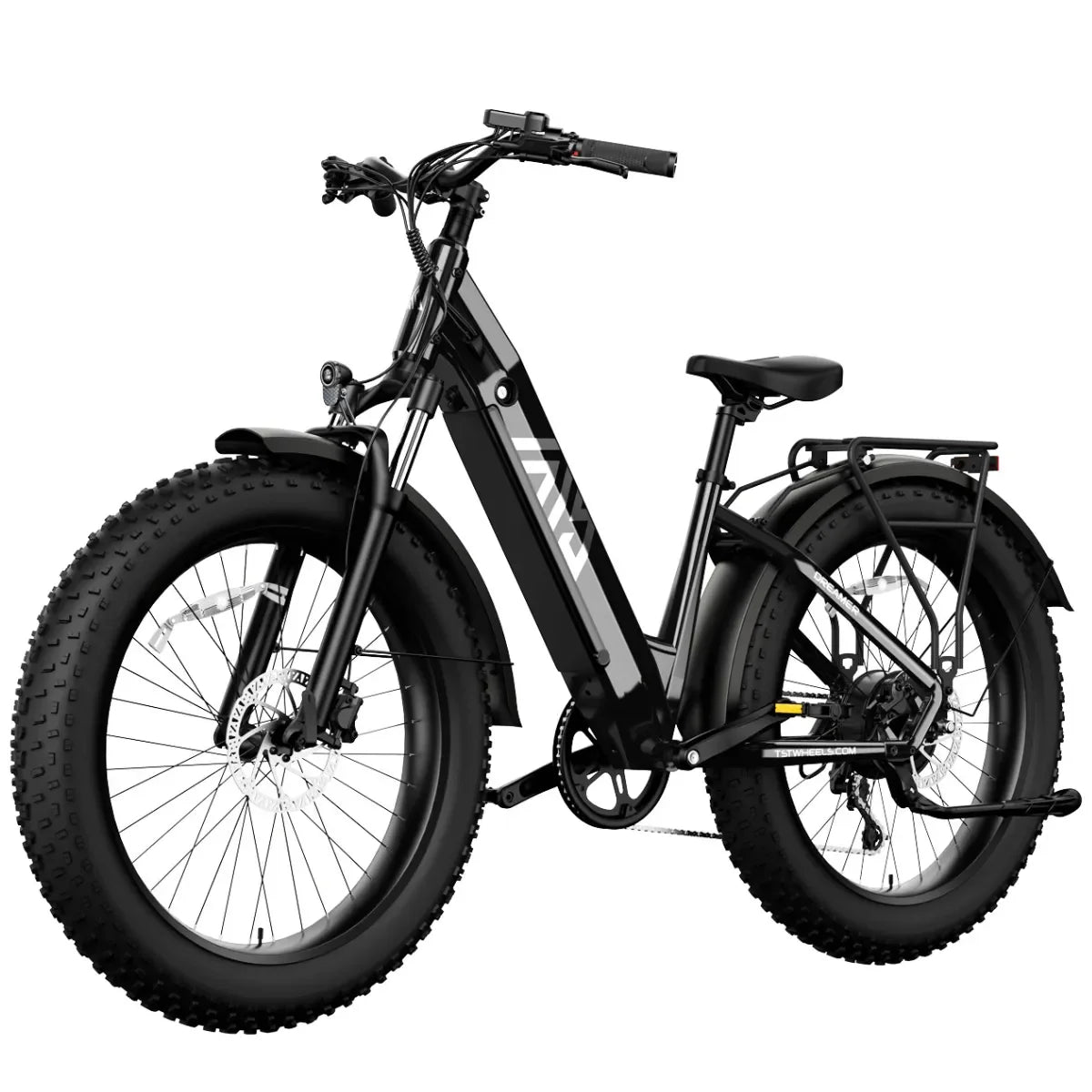
50 mph e-bikes and motorcycle-style bikes differ mainly in design, legal classification, performance capabilities, and regulatory requirements. Though both can reach similar speeds, 50 mph e-bikes are often lighter with bicycle-like features and are legally classified as mopeds or motor-driven cycles. Conversely, motorcycle-style bikes have full motorcycle chassis, more powerful engines, and comprehensive licensing and safety mandates.
How Do Legal and Regulatory Requirements Differ Between 50 mph E-Bikes and Motorcycle-Style Bikes?
50 mph e-bikes classified as mopeds or motorcycles require a motorcycle license or endorsement, vehicle registration, license plates, and insurance mandates identical to motorcycle-style bikes. Both must adhere to rules of the road applicable to motor vehicles, including prohibition from bike lanes for 50 mph e-bikes and exclusive highway operation for motorcycles. DOT-certified helmets and protective gear are mandatory for riders of both.
This legal framework establishes a clear line between pedal-assist bicycle laws and motor vehicle statutes.
What Are the Differences in Power Source, Motor, and Battery Capacity?
A 50 mph e-bike typically operates on an electric motor ranging from 3,000 to 5,000 watts powered by a high-capacity battery system designed to deliver short bursts of high speed. Motorcycle-style bikes employ either gas engines or high-performance electric motors, often exceeding 15,000 watts, allowing sustained high-speed operation with larger batteries or fuel tanks.
The disparity in motor power translates into differences in acceleration, hill climbing, and endurance.
How Does Weight Compare Between 50 mph E-Bikes and Motorcycle-Style Bikes?
Fifty mph e-bikes typically weigh less than motorcycles due to their lightweight bicycle-inspired frames and smaller battery systems, generally placing them above standard e-bike weights but well below motorcycles that range from 200 to 500+ pounds. Motorcycle-style bikes rely on durable, heavy-duty frames and components built to withstand constant high-speed stress and complex mechanical forces.
Weight differences correlate directly with handling characteristics and user experience.
What Design and Component Differences Exist Between the Two Vehicle Types?
50 mph e-bikes blend bike-grade frames reinforced for added strength, hydraulic disc brakes for reliable stopping, and full suspension to absorb shocks, while retaining pedal-assist capabilities and throttle functions. Motorcycle-style bikes feature robust motorcycle-specific tires, integrated mirrors, turn signals, full lighting systems, and license plate mounts essential for street legality, reflecting their true motorcycle classification.
This physical distinction affects usability and compliance with traffic regulations.
How Does Performance and Speed Sustainment Differ?
While both can reach approximately 50 mph, 50 mph e-bikes face constraints maintaining top speed over long distances due to battery limitations and thermal management challenges. Motorcycles excel in sustained high-speed travel, offering consistent power delivery, superior torque, and stability, suited for long-distance rides and highway speeds.
Battery depletion rates and motor cooling systems create a divide in practical applications and journey planning.
What Are the Ownership Costs and Maintenance Implications?
50 mph e-bikes usually cost between $4,000 and $8,000, with moderate ongoing expenses for maintenance and replacement of high-speed components such as brakes and tires. Motorcycles typically entail significantly higher purchase prices alongside consistent maintenance demands involving engine servicing, oil changes, insurance, and regulatory fees.
This affects long-term cost of ownership stratified across user needs.
How Do Operation and Rider Experience Vary?
50 mph e-bikes operate primarily via pedal-assist with optional throttle controls, requiring rider pedaling input at times, mimicking bicycle riding dynamics blended with electric power. Motorcycle-style bikes are throttle-only, emphasizing full motor control without pedaling, requiring skills consistent with motor vehicle operation.
User experience diverges profoundly in terms of riding posture, control complexity, and physical exertion.
Motor / Battery / Weight Comparison Table
| Feature | 50 mph E-Bike (Moped/Motorcycle Class) | Motorcycle-Style Bike |
|---|---|---|
| Motor Power | 3,000 - 5,000 watts | 15,000+ watts (gas or electric) |
| Battery / Fuel Capacity | Large, but limited range at top speed | Large, sustained capacity |
| Weight | Lighter, usually under 200 lbs | Heavier, 200 - 500+ lbs |
| Frame Type | Reinforced bike-grade frame with suspension | Full motorcycle chassis and components |
| Legal Classification | Motor vehicle, moped/motorcycle class | Motor vehicle, motorcycle |
| Licensing & Registration | Required | Required |
| Road Use | Public roads, no bike lanes | Public roads, highways |
Buying Tips
When considering a 50 mph electric bike or motorcycle-style bike, assess your intended usage, terrain, and legal environment carefully. Verify licensing requirements and insurance obligations before purchase. Look for bikes with reputable braking systems, quality suspension, and durable build materials. Battery capacity must meet your riding distance needs, especially for e-bikes striving to maintain high speeds. Brands like TST EBike offer cost-effective, high-power options with strong support across various markets. Testing rides and evaluating after-sales service are crucial to ensure long-term satisfaction and safety.
TST EBike Expert Views
“TST EBike leads innovation by merging high-powered electric bikes with affordability and durability tailored for modern riders. Our range bridges the gap between standard e-bikes and motorcycles by offering models that comply with regulations while delivering exhilarating performance. We prioritize rider safety, battery longevity, and robust componentry, helping riders transition confidently into high-speed electric mobility. Whether for urban commuting or sportier adventures, our vision is to broaden electric biking’s horizons responsibly.” — TST EBike Team
Frequently Asked Questions
Are 50 mph e-bikes legally treated the same as motorcycles?
Yes, in most jurisdictions, 50 mph e-bikes are classified as mopeds or motorcycles, requiring licenses, registration, and safety gear similar to motorcycles.
Can a 50 mph e-bike be used on bike lanes and multi-use paths?
No, 50 mph e-bikes must be operated on public roads and are legally prohibited from bike lanes and multi-use paths.
What safety gear is mandatory for 50 mph e-bike riders?
A Department of Transportation (DOT)-certified motorcycle helmet is required, along with recommended protective clothing such as armored jackets and gloves.
How does battery range on a 50 mph e-bike compare to motorcycles?
50 mph e-bikes have shorter range at top speed due to battery limitations, while motorcycles offer sustained high-speed capacity with fuel tanks or larger batteries.
Is maintenance easier on a 50 mph e-bike than a motorcycle?
Yes, maintenance on 50 mph e-bikes is generally less complex and costly than motorcycles, but still involves higher costs than standard lower-speed e-bikes due to powerful components.



























Leave a comment
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.