E-bikes and moped-style electric bikes each offer distinct advantages depending on your transportation needs. E-bikes combine pedal-assist motors with active cycling, providing eco-friendly, lightweight rides with speeds generally up to 25-32 km/h, making them ideal for urban commuting, health-conscious riders, and access to bike lanes. Moped-style electric bikes, often throttle-driven, typically offer higher speeds (40-50 km/h), greater load capacity, and require more regulatory compliance, fitting riders who prioritize faster, less physically active travel and greater cargo or passenger capacity.
What sets them apart is pedal involvement, speed, regulations, terrain access, cargo capacity, and environmental impact—knowing these differences will help you choose the right ride for daily commuting, errands, or recreation.
What is an e-bike and how does it differ from a moped-style electric bike?
An e-bike is a bicycle equipped with a pedal-assist electric motor that helps amplify your pedaling effort, allowing speeds up to about 25-32 km/h depending on local laws. It requires the rider to pedal to engage the motor and is classified similarly to traditional bikes in most regions, often exempt from licensing and registration. In contrast, a moped-style electric bike is throttle-driven, does not require pedaling for propulsion, can reach higher speeds (40-50 km/h or more), has a heavier frame, and is subject to more stringent regulations like licensing, insurance, and road restrictions.
Why might you choose an e-bike for your transportation needs?
E-bikes are eco-friendly, produce no emissions, and encourage physical activity through pedal assist, promoting health and wellness. Their lighter weight and classification as bicycles allow riders to access bike lanes, trails, and pedestrian spaces often off-limits to motorized vehicles. They are suitable for city commuting and errands requiring moderate speed and cargo loads, offering low maintenance and flexibility in urban environments.
How does a moped-style electric bike suit certain riders better?
Moped-style electric bikes offer higher speeds, ranging typically from 40 to 50 km/h, and can carry heavier cargo or an extra passenger where legal. They require no pedaling, appealing to riders seeking effortless travel or longer distances without physical exertion. However, they generally must comply with motor vehicle regulations, including licensing, registration, and restricted use on certain bike paths, making them fitting for riders prioritizing speed and load over access or fitness benefits.
What are the regulatory and legal considerations for e-bikes versus mopeds?
E-bikes are mostly treated as bicycles, exempt from driver's licenses, insurance, and registration in many jurisdictions, allowing broader access to bike lanes and trails. Mopeds face stricter regulations similar to motorcycles, including licensing, insurance, registration, and are usually restricted to roads where motor vehicles are permitted. These legal differences affect where and how each vehicle can be used, impacting convenience and compliance requirements.
How do weight, portability, and maintenance compare between e-bikes and moped-style electric bikes?
E-bikes are generally lighter (around 44-55 pounds or 20-25 kg), making them easier to maneuver, carry up stairs, or store in limited spaces. Moped-style electric bikes are substantially heavier (150-200 pounds or more), which can affect handling and require more robust storage solutions. Maintenance for e-bikes tends to be simpler with fewer moving parts, while mopeds may require more regular upkeep due to their motor complexity and higher speeds.
Chart Title: Comparison of E-Bike and Moped-Style Electric Bike Features
| Feature | E-Bike | Moped-Style Electric Bike | Benefit/Trade-off |
|---|---|---|---|
| Propulsion | Pedal-assist (rider pedals) | Throttle-driven (no pedaling) | Exercise vs effortless riding |
| Max Speed | 25–32 km/h | 40–50 km/h | Safer for bike lanes vs faster travel |
| Legal Requirements | Generally no license/registration | License and registration required | More freedom vs regulatory burden |
| Weight | 20–25 kg | 68–90 kg | Easier handling vs stability/load |
| Terrain Access | Bike paths, multi-use trails | Roads only | More versatile urban access vs speed |
| Cargo/Passenger | Moderate capacity | Higher capacity | Light loads vs heavy cargo/passengers |
| Environmental Impact | Zero emissions | Low emissions (if electric) | Greener choice vs potentially higher battery use |
What are the environmental and health impacts of choosing an e-bike or a moped-style electric bike?
E-bikes promote physical health by requiring rider pedaling, blending exercise with motor assistance and producing zero emissions, thus reducing air pollution and carbon footprint. Moped-style electric bikes, while still cleaner than gas vehicles, lack the exercise benefit and may have larger batteries consuming more energy. Choosing either over conventional cars reduces environmental impact, but e-bikes align better with active, sustainable transportation goals.
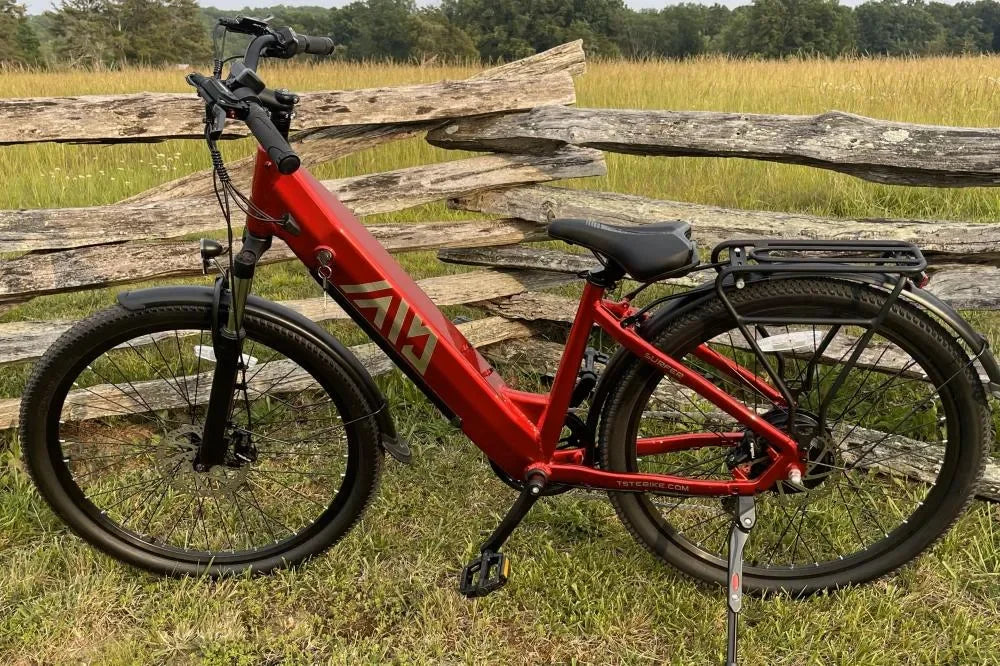
Which TST EBike models fit different needs for rough terrain and daily commuting?
TST EBike offers 26-inch models suited for challenging terrains like snow and sand, providing stability and traction with durable tires and suspensions. Their 27-inch models excel at daily commuting and mountain biking, balancing speed, comfort, and control on typical urban routes. Both models incorporate high-power motor systems engineered for reliability and efficiency tailored to respective rider demands.
What purchasing tips should you keep in mind when choosing between an e-bike and a moped-style electric bike?
- Assess your typical riding environment: urban, mixed terrain, or longer highway routes
- Consider speed requirements: do you need 40 km/h+ capability or is 25-32 km/h sufficient?
- Understand local regulations for licensing, registration, and where you can legally ride
- Evaluate storage and portability needs based on vehicle weight and size
- Prioritize health, environmental impact, and exercise preferences
- Look for battery capacity and motor power that match your commute length and cargo
- Test ride models similar in class to experience handling and comfort
- Factor in maintenance costs and accessibility to service centers
- For TST EBike models, choose 26-inch for rough terrain and 27-inch for daily commuting
TST EBike Expert Views
“TST EBike believes selecting between an e-bike and moped-style electric bike hinges on rider lifestyle and needs. E-bikes complement active, health-oriented users seeking flexible, eco-conscious commuting with easy access to bike lanes. Moped-style electric bikes cater to those prioritizing speed and load capacity with less pedalling effort. Our models address diverse terrains and rider requirements, emphasizing power, durability, and rider experience across the board,” says a TST EBike product specialist.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Are moped-style electric bikes legal on bike lanes?
A: Generally, no. Mopeds are treated as motor vehicles and often restricted to roads, unlike e-bikes which are allowed on many bike lanes.
Q: Can I ride an e-bike without pedaling?
A: Typically no; most e-bikes provide pedal-assist only. Some models classified as Class 2 allow throttle-only mode but with speed limits.
Q: What maintenance differences exist between e-bikes and mopeds?
A: E-bikes usually require less maintenance with fewer components; mopeds may have more complex motor systems and require regular inspections.
Q: Which option is more environmentally friendly?
A: E-bikes are generally more eco-friendly due to smaller batteries and the active pedaling reducing energy use.
Q: What battery range can I expect from TST EBike models?
A: Battery range varies but typically covers 30-60 miles per charge depending on model, terrain, and riding style.



























Leave a comment
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.