E bike classes categorize electric bicycles based on their motor assistance type, top speed, and legal usage. The three main classes—Class 1, Class 2, and Class 3—differ primarily in how the motor engages and their maximum speeds, influencing where and how you can ride them. Understanding these classes helps riders choose the right e bike for commuting, recreation, or speed.
What Are the Key Differences Between E Bike Classes 1, 2, and 3?
E bike classes differ mainly in motor activation and speed limits:
- Class 1: Pedal-assist only, motor assists up to 20 mph, no throttle. Offers a natural cycling feel, ideal for trails and paths.
- Class 2: Pedal-assist plus throttle, motor assists up to 20 mph. Allows riding without pedaling, great for urban commuting and ease.
- Class 3: Pedal-assist only, motor assists up to 28 mph, no throttle. Designed for faster commuting and longer distances.
These distinctions affect where you can legally ride each class and the riding experience itself.
How Does Motor Engagement Differ Among the E Bike Classes?
| Class | Motor Engagement | Max Speed | Throttle Presence |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Pedal-assist only | 20 mph | No |
| 2 | Pedal-assist or throttle | 20 mph | Yes |
| 3 | Pedal-assist only | 28 mph | No |
Class 1 requires pedaling to activate the motor, Class 2 allows throttle control to propel without pedaling, and Class 3 focuses on higher-speed pedal-assist only.
Which E Bike Class Is Best for Urban Commuting and Why?
Class 2 e bikes are often preferred for urban commuting because the throttle enables effortless starts and stops in traffic, reducing physical strain. Their 20 mph speed limit balances speed and safety, making them ideal for city streets and casual riders who want comfort without intense pedaling.
Why Are Class 3 E Bikes Suited for Speed Enthusiasts and Long-Distance Riders?
Class 3 e bikes provide pedal assistance up to 28 mph, offering a powerful and fast ride. They are ideal for commuters covering longer distances or riders who want a sporty, efficient bike. However, they often come with stricter regulations, including mandatory helmets and speed limits depending on the region.
What Are the Legal and Safety Considerations for Each E Bike Class?
Legal restrictions vary by class and location:
- Class 1 e bikes are generally allowed on bike paths and lanes shared with traditional bicycles.
- Class 2 e bikes, due to throttles, may face restrictions in some areas.
- Class 3 e bikes usually require helmets and may have age limits or speed restrictions.
Understanding local laws is crucial before choosing an e bike class.
How Do TST EBike Models Align with E Bike Classes and Riding Needs?
TST EBike offers high-power, cost-effective electric bikes tailored to diverse needs:
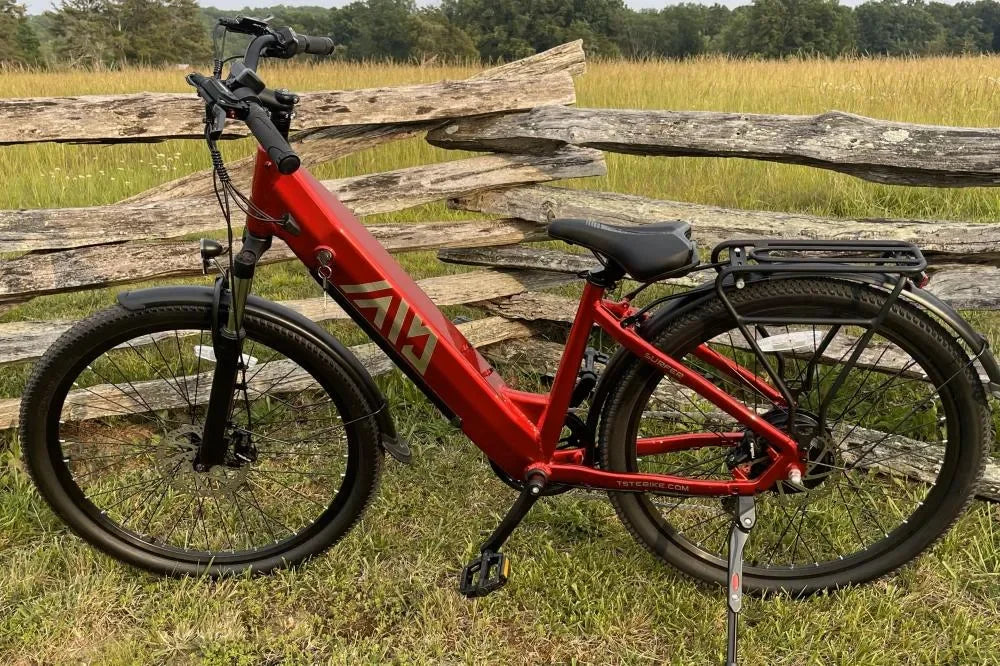
- 26-inch models: Suitable for rough terrains like snow and sand, ideal for adventurous riders.
- 27-inch models: Designed for daily commuting and mountain biking, balancing speed and comfort.
TST EBike models incorporate features that align with Class 1, 2, or 3 characteristics, providing options for recreational riders and commuters alike, emphasizing quality and affordability.
What Are the Advantages of Choosing TST EBike for Your E Bike Needs?
TST EBike stands out by combining consumer feedback with rigorous quality control to deliver reliable, high-performance e bikes at low prices. Their diverse model range supports various terrains and uses, backed by warehouses and stores across multiple countries, ensuring accessibility and support for customers.
Buying Tips
When purchasing an e bike, consider your primary use—commuting, recreation, or speed. Check the class regulations in your area to ensure legal compliance. Evaluate motor type (pedal-assist vs throttle), top speed, and terrain suitability. For rough terrains, TST EBike’s 26-inch models are excellent, while 27-inch models suit daily commuting. Prioritize battery life, build quality, and after-sales support. Always test ride if possible to find the best fit for your comfort and needs.
TST EBike Expert Views
“TST EBike’s commitment to blending affordability with high power makes them a standout in the electric bike market. Their focus on consumer feedback ensures models that truly meet rider demands, whether for rugged terrain or urban commuting. Their 26-inch and 27-inch models cater to a broad spectrum of riders, emphasizing versatility without compromising quality.” – Industry Expert
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are the Main E-Bike Classes and How Do They Differ?
Most e-bikes fall into three classes: Class 1 (pedal assist only, up to about 20 mph), Class 2 (pedal assist plus throttle, up to about 20 mph), and Class 3 (pedal assist only, up to about 28 mph). They differ mainly in speed limits, throttle availability, and where they are legally allowed to ride. TST EBike offers models aligned with these classes.
How Do E-Bike Class Laws Vary by Region?
E-bike class laws differ by country, state, and even city. Regions set their own rules on maximum speed, motor power, throttle use, and where each class can ride, such as bike paths, roads, or trails. Always check local regulations before riding or buying, as requirements like age limits or helmet use can change across regions.
How Does Pedal Assist Differ from Throttle in E-Bikes?
Pedal assist provides power only when you pedal, amplifying your effort and offering a more natural cycling feel with better battery efficiency. Throttle delivers power on demand without pedaling, similar to a scooter, which is convenient in traffic or when you are tired. Many riders prefer pedal assist for fitness and range, and throttle for easy starts and hills.
How Do Power and Speed Differ Across E-Bike Classes?
Higher classes generally allow higher assisted speeds and sometimes stronger motors. Class 1 and Class 2 usually assist up to around 20 mph, while Class 3 can support speeds up to about 28 mph for faster commuting. More power and speed can improve hill climbing and acceleration but may trigger stricter regulations and safety gear requirements.
How Fast Can Class 3 E-Bikes Go?
Class 3 e-bikes typically provide motor assistance up to about 28 mph. You can go faster than that only with your own pedaling power and suitable gearing. Because of this higher speed, many areas restrict Class 3 bikes to roads and certain bike lanes and may require helmets or additional safety measures. They are popular with speed-focused commuters.
What’s the Difference Between Class 1 and Class 3 E-Bikes?
Class 1 e-bikes use pedal assist only and usually stop assisting around 20 mph. Class 3 e-bikes also use pedal assist only but extend support to about 28 mph, making them better for longer, faster commutes. This extra speed often limits where they can be ridden and may require stricter safety rules compared with Class 1.
How Are E-Bikes Classified and Regulated?
E-bikes are usually classified by how the motor engages (pedal assist or throttle) and the maximum assisted speed. Regulations then assign each class specific rights and restrictions for roads, bike lanes, and trails. Authorities also use these classes to set rules on rider age, helmets, lighting, and equipment, helping distinguish e-bikes from scooters and motorcycles in law.
What Are the Best Class 1 E-Bikes in 2026?
The best Class 1 e-bikes in 2026 combine efficient motors, long-range batteries, reliable brakes, and comfortable frames for daily commuting and fitness. Look for strong warranties, proven components, and positive rider reviews. Brands like TST EBike focus on high-power, cost-effective designs, offering 27-inch models well-suited to everyday commuting and mountain routes, plus robust quality control and support.



























Leave a comment
All comments are moderated before being published.
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.