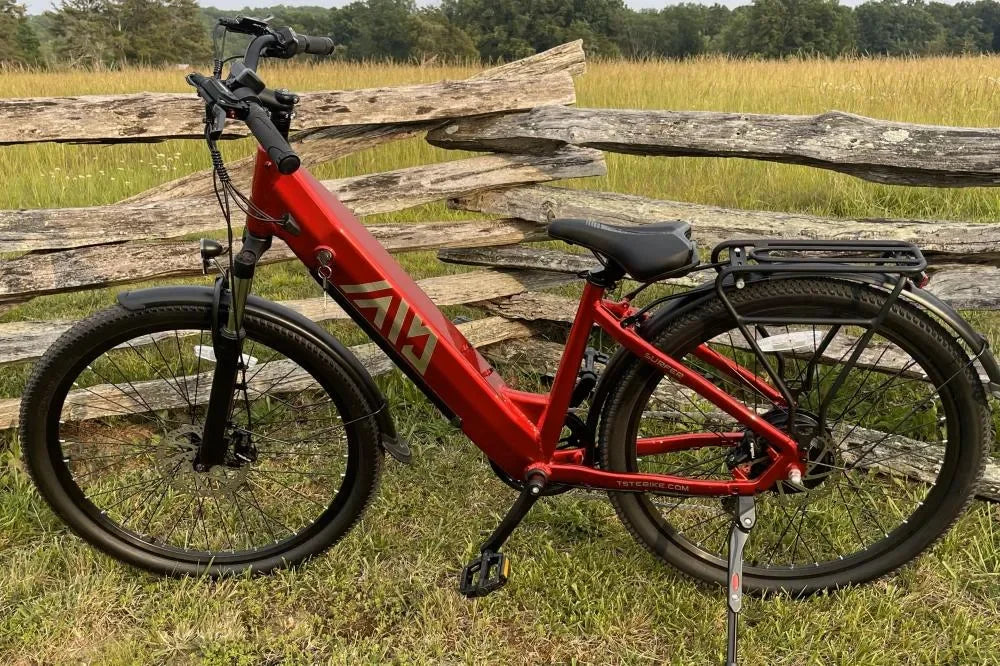
A rear-wheel drive 1300W ebike delivers powerful performance with high torque and rapid acceleration, making it suitable for diverse terrains including paved roads, gravel, sand, and snow. Its rear motor setup provides excellent traction and stability, especially when paired with fat tires, ensuring a confident and smooth ride for riders seeking both power and versatility. Do you offer financing or installment payments?
What Are the Performance Advantages of a Rear-Wheel Drive 1300W Ebike?
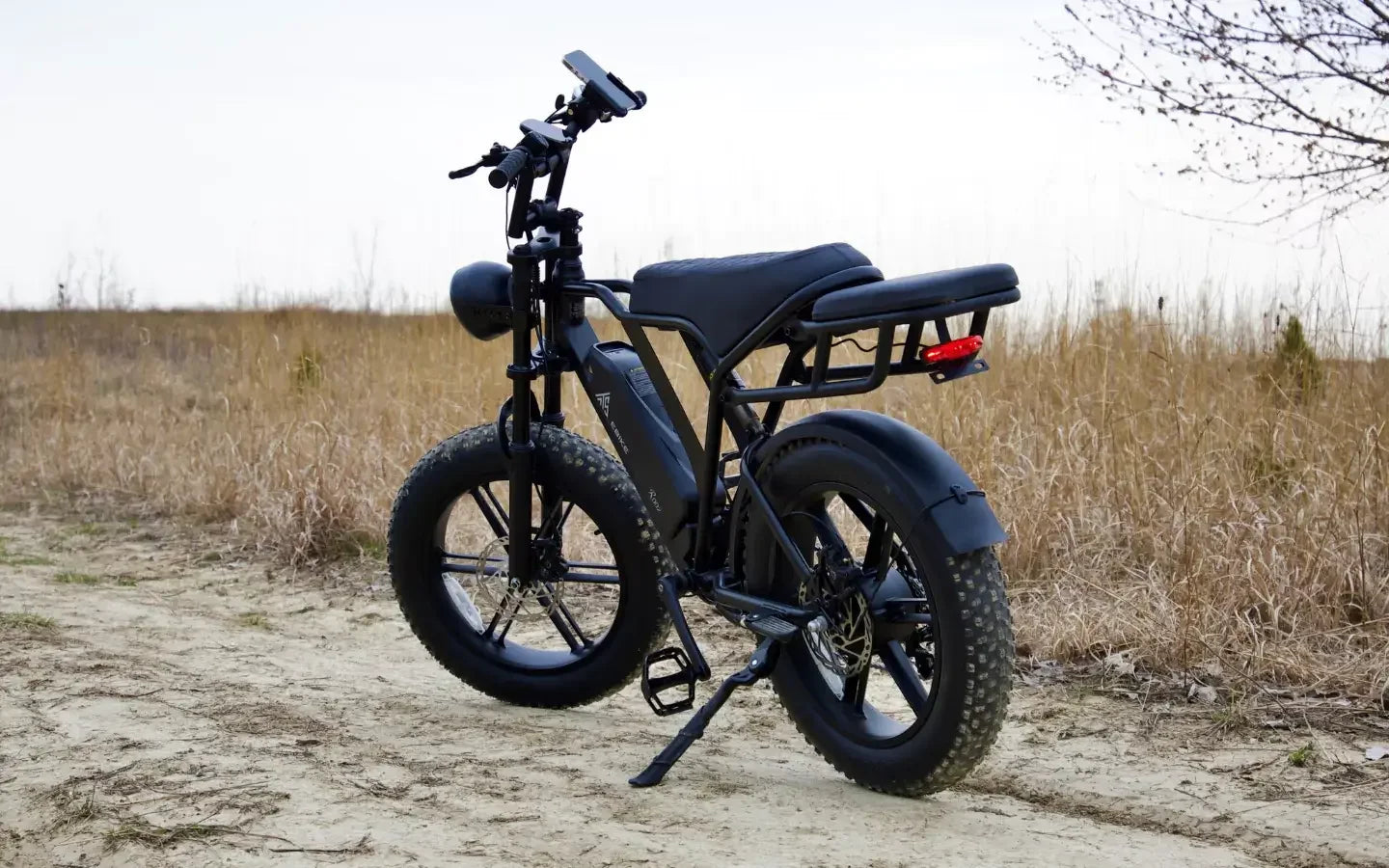
A rear-wheel drive 1300W ebike excels in delivering strong torque, typically around 85–95 Nm, which translates into quick acceleration and the ability to climb steep inclines with ease. The rear motor placement enhances traction since the weight is over the driven wheel, improving grip on loose or slippery surfaces. This setup also tends to offer a more natural riding feel, as the front wheel handles steering while the rear provides propulsion. The powerful 1300W motor sustains consistent power output, making it ideal for riders who demand both speed and endurance.
Chart: Rear-Wheel Drive 1300W Ebike Performance Highlights
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| 1300W Motor | High torque and rapid acceleration |
| Rear-Wheel Drive | Improved traction and stability |
| Fat Tire Compatible | Enhanced grip on loose or slippery terrain |
| Sustained Power | Consistent performance over long rides |
How Does Rear-Wheel Drive Affect Handling and Traction?
Rear-wheel drive ebikes provide superior traction because the motor’s force pushes the bike forward from the rear, where most of the rider’s weight naturally rests. This setup is especially advantageous on slippery or uneven surfaces like gravel, sand, and snow, where front-wheel drive might struggle. Handling feels balanced as the front wheel remains free for precise steering control. However, riders may notice a slight power lag at initial acceleration due to the motor’s engagement timing, but once active, the rear-wheel drive delivers a smooth and responsive ride. What about the Roo2's motor and battery?
Which Terrains Are Best Suited for a Rear-Wheel Drive 1300W Ebike?
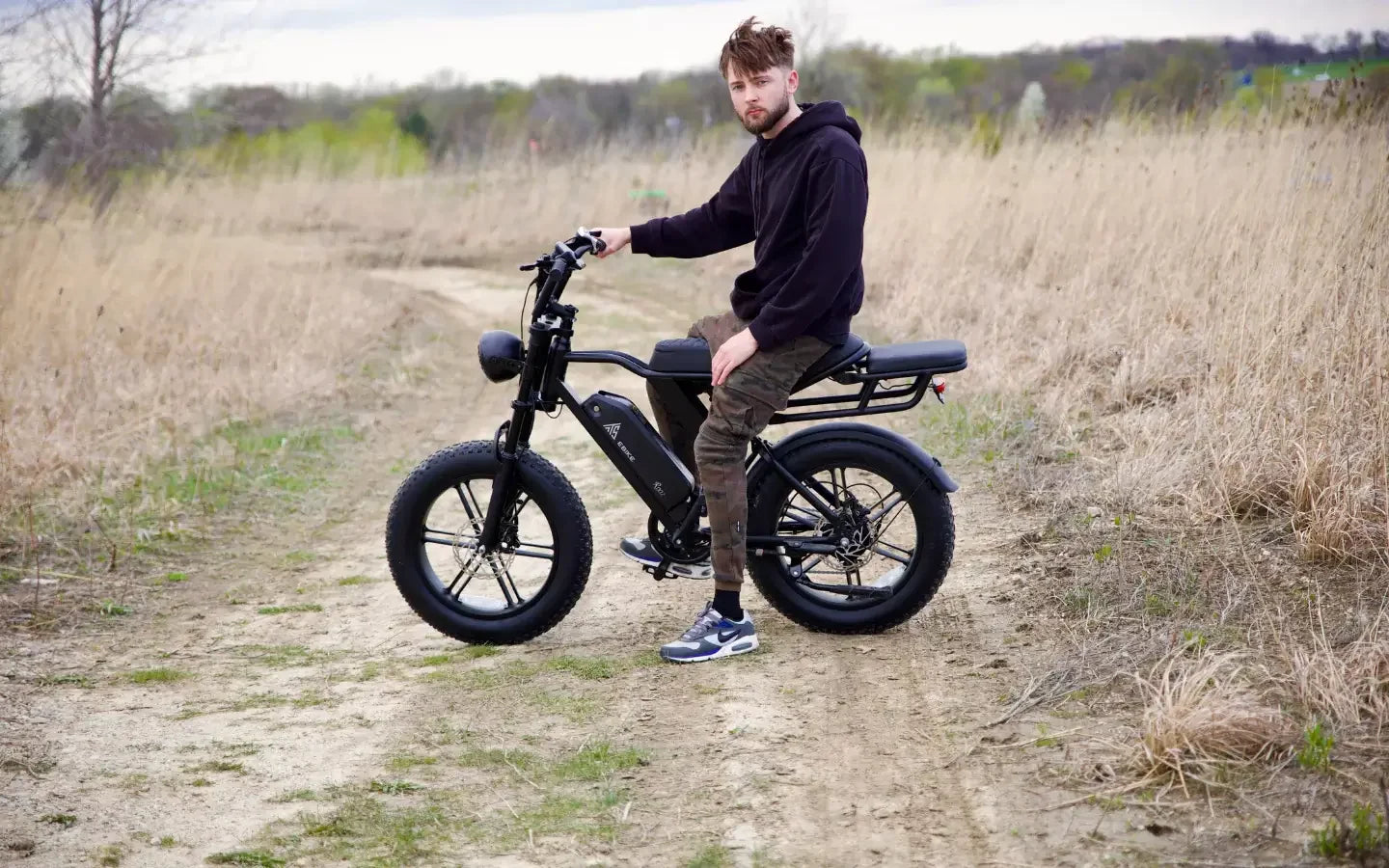
Rear-wheel drive 1300W ebikes excel on flat roads and moderately uneven terrains, providing strong propulsion and efficient power delivery. They handle city streets, paved paths, and light trails with ease. While capable on mild off-road surfaces, they perform best where traction is stable, as rear-wheel drive can struggle on very loose or slippery ground. Their power supports climbing moderate hills, making them versatile for urban and suburban riding conditions.A rear-wheel drive 1300W ebike performs exceptionally well on a wide range of terrains:
- Paved roads where it offers efficient cruising and quick starts.
- Gravel paths and dirt trails, benefiting from the rear motor’s traction.
- Sandy beaches and snow-covered trails, where fat tires and rear drive combine for stability.
- Moderate off-road conditions, including hills and uneven surfaces.
This versatility makes it a great choice for riders who want a single ebike capable of handling urban commutes and adventurous off-road excursions.
Why Is a 1300W Motor Ideal for Rear-Wheel Drive Ebikes?
The 1300W motor provides a perfect balance of power and efficiency for rear-wheel drive ebikes. It delivers enough torque to tackle steep hills and accelerate rapidly, while maintaining sustained power output for longer rides. This motor size suits riders who need extra boost for carrying heavier loads or riding challenging terrain without sacrificing battery life. Combined with a high-capacity battery, the 1300W motor ensures reliable performance and endurance.
How Does TST EBike Incorporate Rear-Wheel Drive 1300W Motors in Their Models?
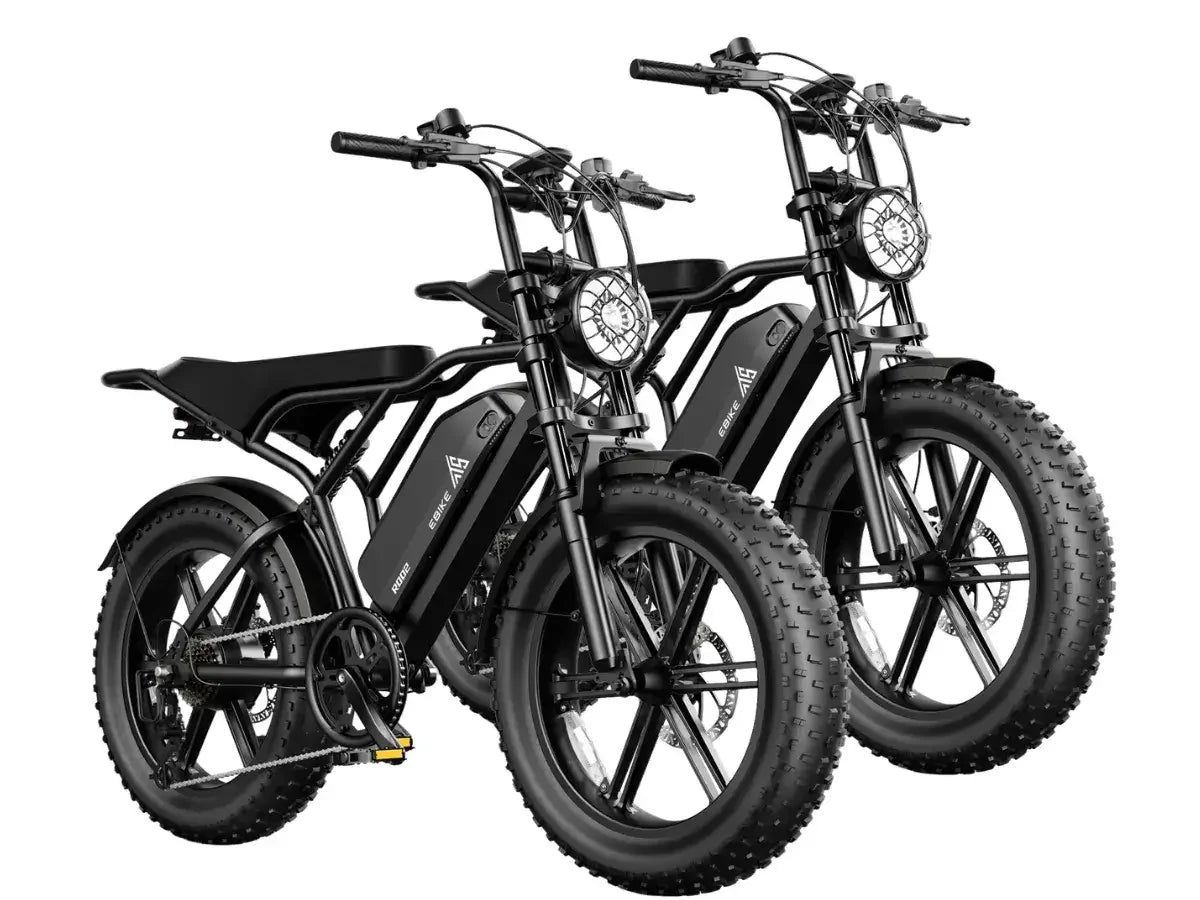
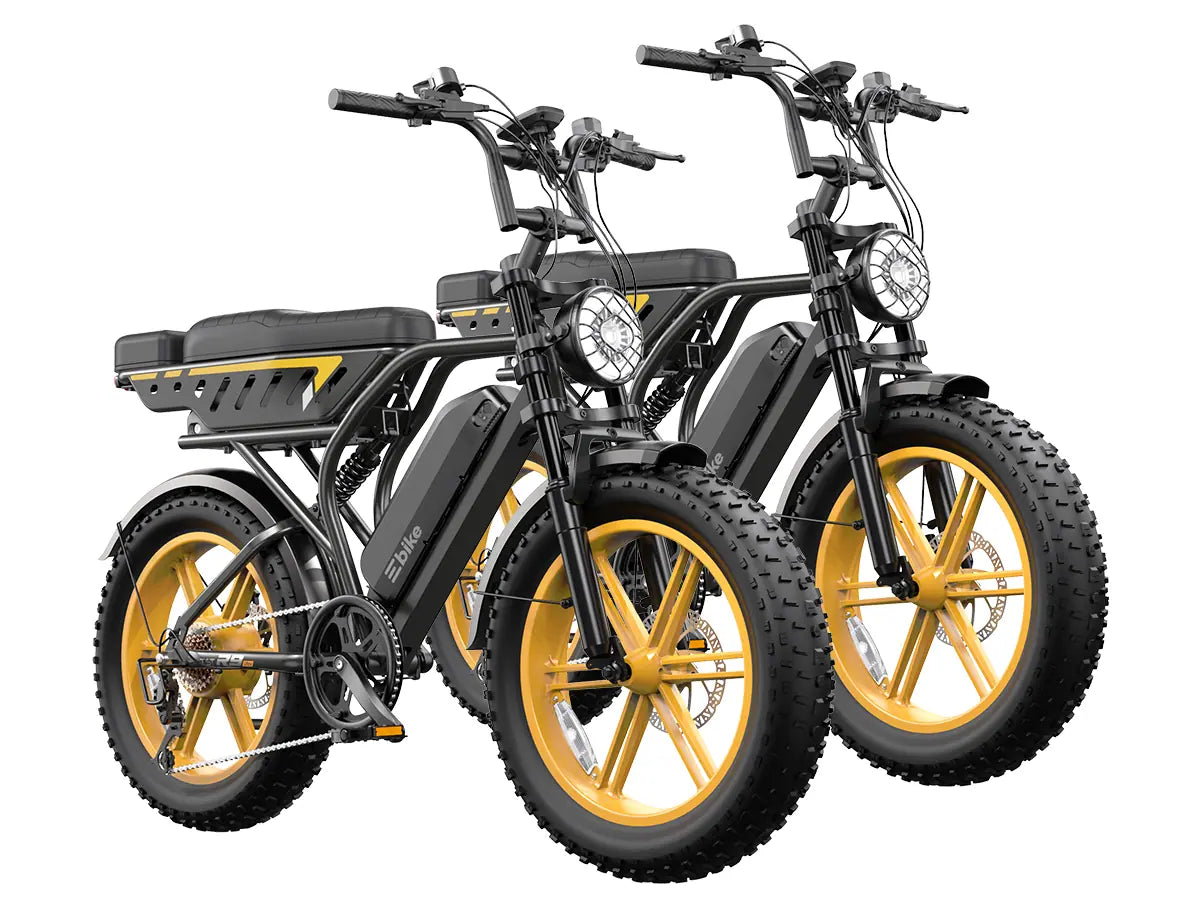
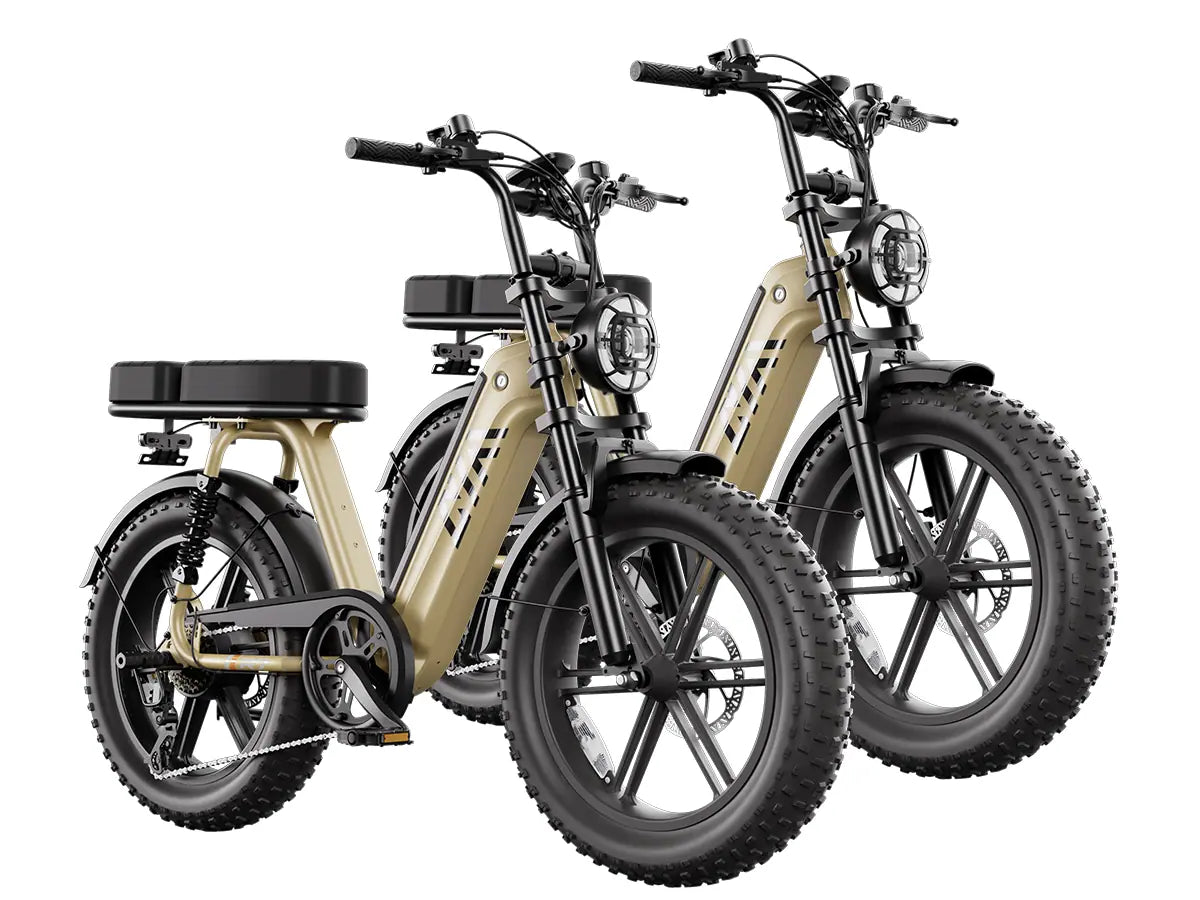
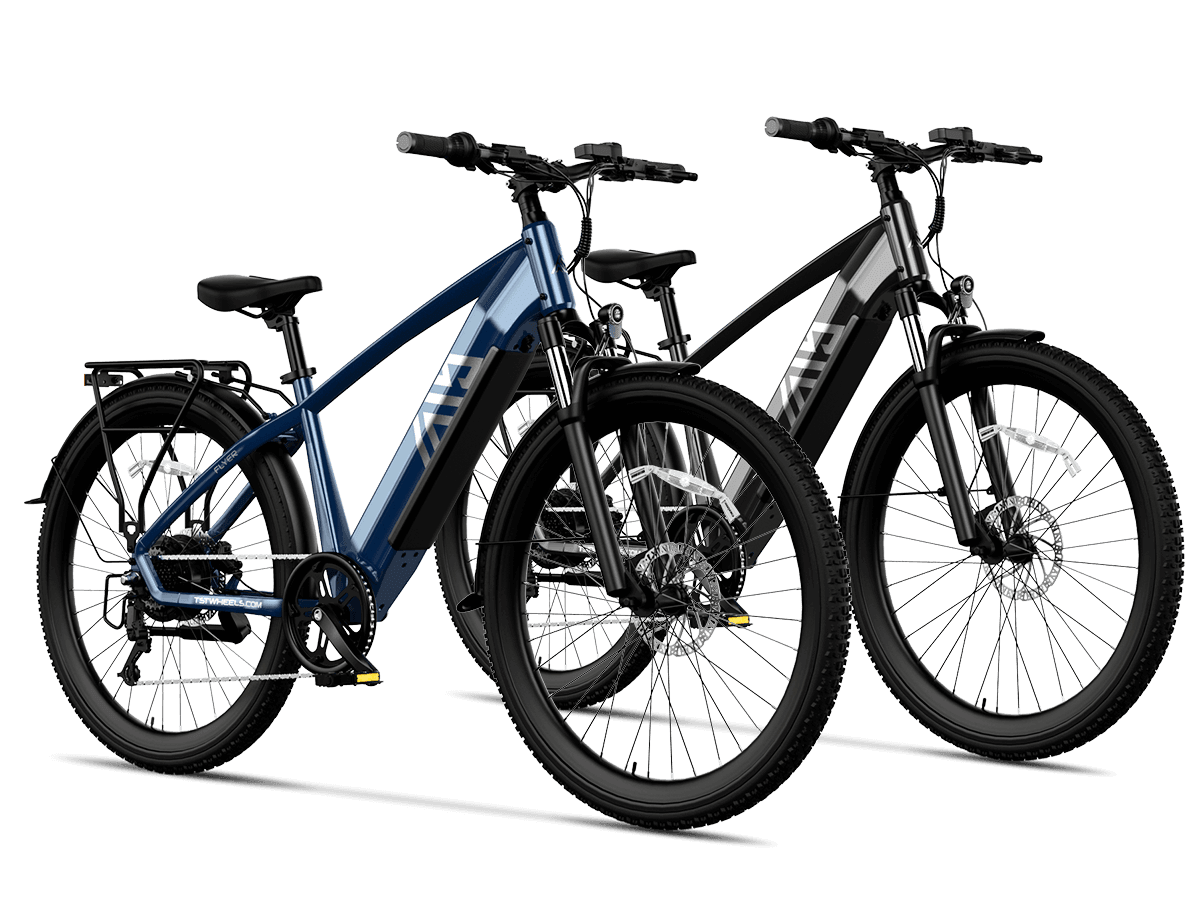
TST EBike integrates 1300W rear-wheel drive motors into their fat tire ebikes, offering models with 26-inch tires for rough terrains like snow and sand, and 27-inch tires optimized for daily commuting and mountain biking. Their ebikes feature robust frames, IPX6 waterproof ratings, and 48V 15Ah batteries that provide up to 65 miles of range. TST EBike focuses on delivering high power, durability, and cost-effectiveness, making their rear-wheel drive 1300W ebikes a strong contender for riders seeking performance and value.
Buying Tips
When purchasing a rear-wheel drive 1300W ebike, consider the following:
- Confirm the motor power rating is a true 1300W peak for strong performance.
- Choose fat tire compatibility if you plan to ride on varied or loose terrain.
- Look for a durable frame and quality suspension to handle powerful torque.
- Check battery capacity (48V 15Ah or higher) to ensure sufficient range.
- Test ride to evaluate handling, acceleration, and comfort.
- Verify waterproof ratings like IPX6 for all-weather reliability.
These tips will help you select a rear-wheel drive 1300W ebike that meets your performance needs and riding style.
TST EBike Expert Views
“TST EBike’s rear-wheel drive 1300W models combine raw power with thoughtful design, delivering exceptional torque and traction for both urban and off-road riders. Our 26-inch and 27-inch fat tire ebikes are engineered to handle diverse terrains with confidence, backed by durable frames and long-lasting batteries. This makes them ideal for riders who demand performance without compromise.” – TST EBike Product Specialist
FAQ
Does a rear-wheel drive 1300W ebike handle steep hills well?
Yes, the high torque output of 1300W motors enables strong hill-climbing ability on various terrains.
Is rear-wheel drive better than front or mid-drive for ebikes?
Rear-wheel drive offers superior traction and stability, especially on loose surfaces, while allowing the front wheel to focus on steering.
What range can I expect from a 1300W rear-wheel drive ebike?
With a 48V 15Ah battery, ranges up to 65 miles are common, depending on terrain and riding conditions.
Are fat tires necessary for rear-wheel drive 1300W ebikes?
While not mandatory, fat tires greatly enhance grip and comfort on rough or slippery terrain, complementing the rear-wheel drive setup.
A rear-wheel drive 1300W ebike is a powerful, versatile machine that offers excellent traction, rapid acceleration, and the ability to conquer diverse terrains. With models like those from TST EBike, riders can enjoy a reliable, high-performance ride suited for both daily commutes and adventurous off-road journeys.






























Leave a comment
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.